Many players in BCL-2 family affairs
- PMID: 24503222
- PMCID: PMC4005919
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2013.12.006
Many players in BCL-2 family affairs
Abstract
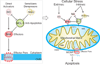
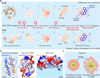
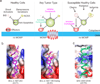
During apoptotic cell death, cellular stress signals converge at the mitochondria to induce mitochondrial outer-membrane permeabilization (MOMP) through B cell lymphoma-2 (BCL-2) family proteins and their effectors. BCL-2 proteins function through protein-protein interactions, the mechanisms and structural aspects of which are only now being uncovered. Recently, the elucidation of the dynamic features underlying their function has highlighted their structural plasticity and the consequent complex thermodynamic landscape governing their protein-protein interactions. These studies show that canonical interactions involve a conserved, hydrophobic groove, whereas non-canonical interactions function allosterically outside the groove. We review the latest structural advances in understanding the interactions and functions of mammalian BCL-2 family members, and discuss new opportunities to modulate these proteins in health and disease.
Keywords: B cell lymphoma-2 (BCL-2) family proteins; mitochondrial apoptosis; mitochondrial outer-membrane permeabilization (MOMP).
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Green DR. Apoptotic pathways: ten minutes to dead. Cell. 2005;121:671–674. - PubMed
-
- Jiang X, Wang X. Cytochrome C-mediated apoptosis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004;73:87–106. - PubMed
-
- Enari M, et al. A caspase-activated DNase that degrades DNA during apoptosis, and its inhibitor ICAD. Nature. 1998;391:43–50. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki J, et al. Xk-related protein 8 and CED-8 promote phosphatidylserine exposure in apoptotic cells. Science. 2013;341:403–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

