Abdominal aortic intimal flap motion characterization in acute aortic dissection: assessed with retrospective ECG-gated thoracoabdominal aorta dual-source CT angiography
- PMID: 24503676
- PMCID: PMC3913653
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087664
Abdominal aortic intimal flap motion characterization in acute aortic dissection: assessed with retrospective ECG-gated thoracoabdominal aorta dual-source CT angiography
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the feasibility of dose-modulated retrospective ECG-gated thoracoabdominal aorta CT angiography (CTA) assessing abdominal aortic intimal flap motion and investigate the motion characteristics of intimal flap in acute aortic dissection (AAD).
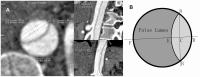
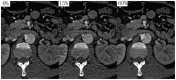
Materials and methods: 49 patients who had thoracoabdominal aorta retrospective ECG-gated CTA scan were enrolled. 20 datasets were reconstructed in 5% steps between 0 and 95% of the R-R interval in each case. The aortic intimal flap motion was assessed by measuring the short axis diameters of the true lumen and false lumen 2 cm above of celiac trunk ostium in different R-R intervals. Intimal flap motion and configuration was assessed by two independent observers.
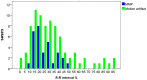
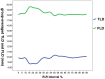
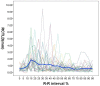
Results: In these 49 patients, 37 had AAD, 7 had intramural hematoma, and 5 had negative result for acute aortic disorder. 620 datasets of 31 patients who showed double lumens in abdominal aorta were enrolled in evaluating intimal flap motion. The maximum and minimum true lumen diameter were 12.2 ± 4.1 mm (range 2.6 ∼ 17.4) and 6.7 ± 4.1 mm (range 0 ∼ 15.3) respectively. The range of intimal flap motion in all patients was 5.5 ± 2.6 mm (range 1.8 ∼ 10.2). The extent of maximum true lumen diameter decreased during a cardiac cycle was 49.5% ± 23.5% (range 12% ∼ 100%). The maximum motion phase of true lumen diameter was in systolic phase (5% ∼ 40% of R-R interval). Maximum and minimum intimal flap motion was at 15% and 75% of the R-R interval respectively. Intimal flap configuration had correlation with the phase of cardiac cycle.
Conclusions: Abdominal intimal flap position and configuration varied greatly during a cardiac cycle. Retrospective ECG-gated thoracoabdominal aorta CTA can reflect the actual status of the true lumen and provide more information about true lumen collapse. This information may be helpful to diagnosis and differential diagnosis of dynamic abstraction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detection of the intimal tear in aortic dissection and ulcer-like projection in intramural hematoma: usefulness of full-phase retrospective ECG-gated CT angiography.Jpn J Radiol. 2020 Nov;38(11):1036-1045. doi: 10.1007/s11604-020-01008-1. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Jpn J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32710132 Free PMC article.
-
Motion characterization of aortic wall and intimal flap by ECG-gated CT in patients with chronic B-dissection.Eur J Radiol. 2009 Oct;72(1):146-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2008.06.024. Epub 2008 Aug 3. Eur J Radiol. 2009. PMID: 18678452
-
Significance of systolic-phase imaging on full-phase ECG-gated CT angiography to detect intimal tears in aortic dissection.Heart Vessels. 2022 Nov;37(11):1947-1956. doi: 10.1007/s00380-022-02093-0. Epub 2022 May 15. Heart Vessels. 2022. PMID: 35569067 Free PMC article.
-
Role of transesophageal echocardiography in dissection of the aorta and evaluation of degenerative aortic disease.Cardiol Clin. 1993 Aug;11(3):461-73. Cardiol Clin. 1993. PMID: 8402774 Review.
-
Acute aortic syndromes: new insights from electrocardiographically gated computed tomography.Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008 Winter;20(4):340-7. doi: 10.1053/j.semtcvs.2008.11.011. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008. PMID: 19251175 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Residual Intimal Flap Displacement Post-TEVAR on TBAD Haemodynamics in Compliant, Patient-specific CFD Simulations Informed by MRI.Ann Biomed Eng. 2025 Aug;53(8):1834-1851. doi: 10.1007/s10439-025-03739-6. Epub 2025 May 9. Ann Biomed Eng. 2025. PMID: 40346352 Free PMC article.
-
High intimal flap mobility assessed by intravascular ultrasound is associated with better short-term results after TEVAR in chronic aortic dissection.Sci Rep. 2019 May 13;9(1):7267. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43856-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31086282 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of the intimal tear in aortic dissection and ulcer-like projection in intramural hematoma: usefulness of full-phase retrospective ECG-gated CT angiography.Jpn J Radiol. 2020 Nov;38(11):1036-1045. doi: 10.1007/s11604-020-01008-1. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Jpn J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32710132 Free PMC article.
-
Aortic dissection simulation models for clinical support: fluid-structure interaction vs. rigid wall models.Biomed Eng Online. 2015 Apr 15;14:34. doi: 10.1186/s12938-015-0032-6. Biomed Eng Online. 2015. PMID: 25881252 Free PMC article.
-
CT angiography in the diagnosis of cardiovascular disease: a transformation in cardiovascular CT practice.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2014 Oct;4(5):376-96. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2014.10.02. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2014. PMID: 25392823 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hagan PG, Nienaber CA, Isselbacher EM, Bruckman D, Karavite DJ, et al. (2000) The International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD): new insights into an old disease. JAMA 283: 897–903. - PubMed
-
- Deeb GM, Patel HJ, Williams DM (2010) Treatment for malperfusion syndrome in acute type A and B aortic dissection: A long-term analysis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 140: S98–S100. - PubMed
-
- Yagdi T, Atay Y, Engin C, Mahmudov R, Tetik O, et al. (2006) Impact of organ malperfusion on mortality and morbidity in acute type A aortic dissections. J Card Surg. 2006 21: 363–369. - PubMed
-
- Patel HJ, Williams DM, Dasika NL, Suzuki Y, Deeb GM (2008) Operative delay for peripheral malperfusion syndrome in acute type A aortic dissection: a long-term analysis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 135: 1288–1295. - PubMed
-
- Williams DM, Lee DY, Hamilton BH, Marx MV, Narasimham DL, et al. (1997) The dissected aorta: part III, Anatomy and radiologic diagnosis of branch-vessel compromise. Radiology 203: 37–44. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

