Induction of phagocytosis and intracellular signaling by an inhibitory channel catfish leukocyte immune-type receptor: evidence for immunoregulatory receptor functional plasticity in teleosts
- PMID: 24504017
- PMCID: PMC6741615
- DOI: 10.1159/000356963
Induction of phagocytosis and intracellular signaling by an inhibitory channel catfish leukocyte immune-type receptor: evidence for immunoregulatory receptor functional plasticity in teleosts
Abstract
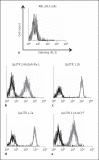
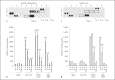
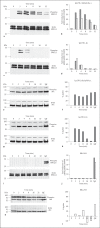
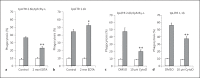
Immunoregulatory receptors are categorized as stimulatory or inhibitory based on their engagement of unique intracellular signaling networks. These proteins also display functional plasticity, which adds versatility to the control of innate immunity. Here we demonstrate that an inhibitory catfish leukocyte immune-type receptor (IpLITR) also displays stimulatory capabilities in a representative myeloid cell model. Previously, the receptor IpLITR 1.1b was shown to inhibit natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Here we expressed IpLITR 1.1b in rat basophilic leukemia-2H3 cells and monitored intracellular signaling and functional responses. Although IpLITR 1.1b did not stimulate cytokine secretion, activation of this receptor unexpectedly induced phagocytosis as well as extracellular signal-related kinase 1/2- and protein kinase B (Akt)-dependent signal transduction. This novel IpLITR 1.1b-mediated response was independent of an association with the FcRγ chain and was likely due to phosphotyrosine-dependent adaptors associating with prototypical signaling motifs within the distal region of its cytoplasmic tail. Furthermore, compared to a stimulatory IpLITR, IpLITR 1.1b displayed temporal differences in the induction of intracellular signaling, and IpLITR 1.1b-mediated phagocytosis had reduced sensitivity to EDTA and cytochalasin D. Overall, this is the first demonstration of functional plasticity for teleost LITRs, a process likely important for the fine-tuning of conserved innate defenses.
© 2014 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Imaging flow cytometry and GST pulldown assays provide new insights into channel catfish leukocyte immune-type receptor-mediated phagocytic pathways.Dev Comp Immunol. 2017 Feb;67:126-138. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2016.10.011. Epub 2016 Oct 28. Dev Comp Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27984101
-
Examination of the stimulatory signaling potential of a channel catfish leukocyte immune-type receptor and associated adaptor.Dev Comp Immunol. 2012 Jan;36(1):62-73. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2011.06.004. Epub 2011 Jun 15. Dev Comp Immunol. 2012. PMID: 21703302
-
Trypsin differentially modulates the surface expression and function of channel catfish leukocyte immune-type receptors.Dev Comp Immunol. 2016 Dec;65:231-244. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2016.07.014. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Dev Comp Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27461858
-
Teleost leukocyte immune-type receptors.Dev Comp Immunol. 2023 Oct;147:104768. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2023.104768. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Dev Comp Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37414235 Review.
-
Biochemical and Functional Insights into the Integrated Regulation of Innate Immune Cell Responses by Teleost Leukocyte Immune-Type Receptors.Biology (Basel). 2016 Mar 8;5(1):13. doi: 10.3390/biology5010013. Biology (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27005670 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of distinct LRC- and Fc receptor complex-like chromosomal regions in fish supports that teleost leukocyte immune-type receptors are distant relatives of mammalian Fc receptor-like molecules.Immunogenetics. 2021 Feb;73(1):93-109. doi: 10.1007/s00251-020-01193-3. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Immunogenetics. 2021. PMID: 33410929 Review.
-
Selective Regulation of Cytoskeletal Dynamics and Filopodia Formation by Teleost Leukocyte Immune-Type Receptors Differentially Contributes to Target Capture During the Phagocytic Process.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 28;9:1144. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01144. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30002653 Free PMC article.
-
Foodies of Innate Immunity.J Innate Immun. 2015;7(4):331-2. doi: 10.1159/000430800. Epub 2015 May 13. J Innate Immun. 2015. PMID: 25997480 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Bacterial phagocytosis and reactive oxygen species production by camel neutrophils and monocytes are influenced by the type of anticoagulation agent.Vet World. 2021 Jul;14(7):1888-1893. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2021.1888-1893. Epub 2021 Jul 24. Vet World. 2021. PMID: 34475713 Free PMC article.
-
A Fish Leukocyte Immune-Type Receptor Uses a Novel Intracytoplasmic Tail Networking Mechanism to Cross-Inhibit the Phagocytic Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 21;21(14):5146. doi: 10.3390/ijms21145146. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32708174 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steevels TAM, Meyaard L. Immune inhibitory receptors: essential regulators of phagocyte function. Eur J Immunol. 2011;41:575–587. - PubMed
-
- Takai T. Fc receptors and their role in immune regulation and autoimmunity. J Clin Immunol. 2005;25:1–18. - PubMed
-
- Barclay AN. Membrane proteins with immunoglobulin-like domains - a master superfamily of interaction molecules. Semin Immunol. 2003;14:215–223. - PubMed
-
- Weis WI, Taylor ME, Drickamer K. The C-type lectin superfamily in the immune system. Immunol Rev. 1998;163:19–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

