Plant chromatin warms up in Madrid: meeting summary of the 3rd European Workshop on Plant Chromatin 2013, Madrid, Spain
- PMID: 24504145
- PMCID: PMC4121374
- DOI: 10.4161/epi.28094
Plant chromatin warms up in Madrid: meeting summary of the 3rd European Workshop on Plant Chromatin 2013, Madrid, Spain
Abstract
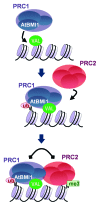
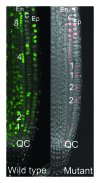
The 3rd European Workshop on Plant Chromatin (EWPC) was held on August 2013 in Madrid, Spain. A number of different topics on plant chromatin were presented during the meeting, including new factors mediating Polycomb Group protein function in plants, chromatin-mediated reprogramming in plant developmental transitions, the role of histone variants, and newly identified chromatin remodeling factors. The function of interactions between chromatin and transcription factors in the modulation of gene expression, the role of chromatin dynamics in the control of nuclear processes and the influence of environmental factors on chromatin organization were also reported. In this report, we highlight some of the new insights emerging in this growing area of research, presented at the 3rd EWPC.
Keywords: chromatin; chromatin reprogramming; development; epigenetics; plants.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
