Risk factors for cerebrovascular disease mortality among the elderly in Beijing: a competing risk analysis
- PMID: 24504327
- PMCID: PMC3913670
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087884
Risk factors for cerebrovascular disease mortality among the elderly in Beijing: a competing risk analysis
Abstract
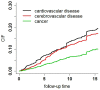
Objective: To examine the associations of combined lifestyle factors and physical conditions with cerebrovascular diseases (CBVD) mortality, after accounting for competing risk events, including death from cardiovascular diseases, cancers and other diseases.
Methods: Data on 2010 subjects aged over 55 years were finally analyzed using competing risk models. All the subjects were interviewed by the Beijing Longitudinal Study of Aging (BLSA), in China, between 1 January 1992 and 30 August 2009.
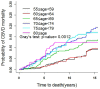
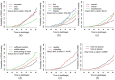
Results: Elderly females were at a lower risk of death from CBVD than elderly males (HR = 0.639, 95% CI = 0.457-0.895). Increasing age (HR = 1.543, 95% CI = 1.013-2.349), poor self-rated health (HR = 1.652, 95% CI = 1.198-2.277), hypertension (HR = 2.201, 95% CI = 1.524-3.178) and overweight (HR = 1.473, 95% CI = 1.013-2.142) or obesity (HR = 1.711, 95% CI = 1.1754-2.490) was associated with higher CBVD mortality risk. Normal cognition function (HR = 0.650, 95% CI = 0.434-0.973) and living in urban (HR = 0.456, 95% CI = 0.286-0.727) was associated with lower CBVD mortality risk. Gray's test also confirmed the cumulative incidence (CIF) of CBVD was lower in the 'married' group than those without spouse, and the mortality was lowest in the 'nutrition sufficient' group among the 'frequent consumption of meat group' and the 'medial type group' (P value<0.001).
Conclusions: CBVD mortality was associated with gender, age, blood pressure, residence, BMI, cognitive function, nutrition and the result of self-rated health assessment in the elderly in Beijing, China.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Feigin VL, Lawes CM, Bennett DA, Barker-Collo SL, Parag V (2009) Worldwide stroke incidence and early case fatality reported in 56 population-based studies: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol 8: 355–369. - PubMed
-
- WHO (2011) The top 10 causes of death. Available: http://who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/(Updated June 2011).
-
- Jiang Y, Li XY, Hu N, Huang ZJ, Wu F (2010) Epidemiologic characteristics of cerebrovascular disease mortality in China, 2004–2005. Zhong Hua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 44: 293–297. - PubMed
-
- He J, Gu D, Wu X, Reynolds K, Duan X, et al. (2005) Major causes of death among men and women in China. The New England Journal of Medicine 353: 1124–34. - PubMed
-
- Flicker L (2010) Cardiovascular risk factors, cerebrovascular disease burden, and healthy brain aging. Clin Geriatr Med 26: 17–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources