Functional and symptom impact of trametinib versus chemotherapy in BRAF V600E advanced or metastatic melanoma: quality-of-life analyses of the METRIC study
- PMID: 24504441
- PMCID: PMC4433512
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdt580
Functional and symptom impact of trametinib versus chemotherapy in BRAF V600E advanced or metastatic melanoma: quality-of-life analyses of the METRIC study
Abstract
Background: In a randomized phase III study, trametinib prolonged progression-free survival and improved overall survival versus chemotherapy in patients with BRAF V600 mutation-positive melanoma.
Patients and methods: Patients' quality of life (QOL) was assessed at baseline and follow-up visits using the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Core QOL questionnaire.
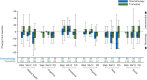
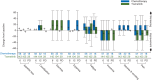
Results: In the primary efficacy population (BRAF V600E+, no brain metastases) from baseline to weeks 6 and 12, patients' global health status scores worsened by 4-5 points with chemotherapy but improved by 2-3 points with trametinib. Rapid and substantive reductions in QOL functionality (e.g. role functioning, 8-11 points at weeks 6 and 12) and symptom exacerbation (e.g. fatigue, 4-8 points; nausea and vomiting, 5 points, both at weeks 6 and 12) were observed in chemotherapy-treated patients. In contrast, trametinib-treated patients reported small improvements or slight worsening from baseline at week 12, depending on the functional dimension and symptom. The mean symptom-scale scores for chemotherapy-treated patients increased from baseline (symptoms worsened) for seven of eight symptoms at week 6 (except insomnia) and six of eight symptoms at week 12 (except dyspnea and insomnia). In contrast, at weeks 6 and 12, the mean symptom-scale scores for trametinib decreased from baseline (symptoms improved) for pain (11-12 points), insomnia (10-12 points), and appetite loss (1-5 points), whereas those for diarrhea worsened (15-16 points). Mixed-model repeated-measures analyses showed significant (P < 0.05) and/or clinically meaningful improvements (small to moderate) from baseline in favor of trametinib for global health; physical, role, and social functioning; fatigue; pain; insomnia; nausea and vomiting; constipation; dyspnea; and appetite at weeks 6 and/or 12. QOL results for the intent-to-treat population were consistent.
Conclusions: This first QOL assessment for a MEK inhibitor in metastatic melanoma demonstrated that trametinib was associated with less functional impairment, smaller declines in health status, and less exacerbation of symptoms versus chemotherapy.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01245062.
Keywords: BRAF; MEK; chemotherapy; melanoma; quality of life; trametinib.
Figures
References
-
- Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature. 2002;417:949–954. - PubMed
-
- Montagut C, Settleman J. Targeting the RAF-MEK-ERK pathway in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2009;283:125–134. - PubMed
-
- Flaherty KT, Robert C, Hersey P, et al. Improved survival with MEK inhibition in BRAF-mutated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:107–114. - PubMed
-
- European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer. EORTC quality of life questionnaire (EORTC QLQ-C30) http://groups.eortc.be/qol/eortc-qlq-c30 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

