Renal angiomyolipoma: a radiological classification and update on recent developments in diagnosis and management
- PMID: 24504542
- PMCID: PMC4040184
- DOI: 10.1007/s00261-014-0083-3
Renal angiomyolipoma: a radiological classification and update on recent developments in diagnosis and management
Abstract
Angiomyolipoma is the most common benign solid renal neoplasm observed in clinical practice. Once thought to be a hamartoma and almost always diagnosed by the imaged-based detection of fat, angiomyolipomas are now known to consist of a heterogeneous group of neoplasms. Although all are considered perivascular epithelioid cell tumors, many display different pathology, imaging features, and clinical behavior. The importance of understanding this group of neoplasms is emphasized by the fact that many types of angiomyolipoma contain little to no fat, and despite being benign, sometimes escape a pre-operative diagnosis. These types of angiomyolipomas can all be considered when encountering a renal mass that is both hyperattenuating relative to renal parenchyma on unenhanced CT and T2-hypointense, features that reflect their predominant smooth muscle component. We review recent developments and provide a radiological classification of angiomyolipomas that helps physicians understand the various types and learn how to both diagnose and manage them.
Figures
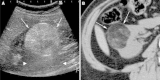
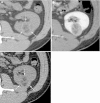
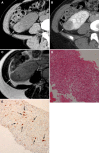
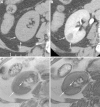

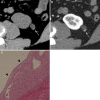

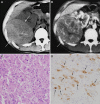
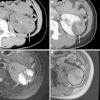
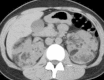
References
-
- Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI, Sesterhenn IA. World Health Organization classification of tumors: pathology and genetics. Tumors of the urinary system and male genital organs. Lyon: IARC Press; 2004.
-
- Jinzaki M, Tanimoto A, Narimatsu Y, et al. Angiomyolipoma: imaging findings in lesions with minimal fat. Radiology. 1997;205:497–502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

