Virtual screening of integrase inhibitors by large scale binding free energy calculations: the SAMPL4 challenge
- PMID: 24504704
- PMCID: PMC4137862
- DOI: 10.1007/s10822-014-9711-9
Virtual screening of integrase inhibitors by large scale binding free energy calculations: the SAMPL4 challenge
Abstract
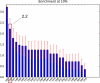
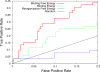
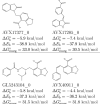
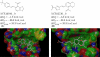
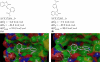
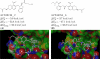
As part of the SAMPL4 blind challenge, filtered AutoDock Vina ligand docking predictions and large scale binding energy distribution analysis method binding free energy calculations have been applied to the virtual screening of a focused library of candidate binders to the LEDGF site of the HIV integrase protein. The computational protocol leveraged docking and high level atomistic models to improve enrichment. The enrichment factor of our blind predictions ranked best among all of the computational submissions, and second best overall. This work represents to our knowledge the first example of the application of an all-atom physics-based binding free energy model to large scale virtual screening. A total of 285 parallel Hamiltonian replica exchange molecular dynamics absolute protein-ligand binding free energy simulations were conducted starting from docked poses. The setup of the simulations was fully automated, calculations were distributed on multiple computing resources and were completed in a 6-weeks period. The accuracy of the docked poses and the inclusion of intramolecular strain and entropic losses in the binding free energy estimates were the major factors behind the success of the method. Lack of sufficient time and computing resources to investigate additional protonation states of the ligands was a major cause of mispredictions. The experiment demonstrated the applicability of binding free energy modeling to improve hit rates in challenging virtual screening of focused ligand libraries during lead optimization.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Virtual screening with AutoDock Vina and the common pharmacophore engine of a low diversity library of fragments and hits against the three allosteric sites of HIV integrase: participation in the SAMPL4 protein-ligand binding challenge.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2014 Apr;28(4):429-441. doi: 10.1007/s10822-014-9709-3. Epub 2014 Feb 4. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2014. PMID: 24493410 Free PMC article.
-
Exhaustive docking and solvated interaction energy scoring: lessons learned from the SAMPL4 challenge.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2014 Apr;28(4):417-27. doi: 10.1007/s10822-014-9715-5. Epub 2014 Jan 29. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2014. PMID: 24474162
-
Virtual screening of the SAMPL4 blinded HIV integrase inhibitors dataset.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2014 Apr;28(4):455-62. doi: 10.1007/s10822-014-9707-5. Epub 2014 Jan 24. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2014. PMID: 24458507
-
Blind prediction of HIV integrase binding from the SAMPL4 challenge.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2014 Apr;28(4):327-45. doi: 10.1007/s10822-014-9723-5. Epub 2014 Mar 5. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2014. PMID: 24595873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Docking.Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(42):7555-7580. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180904115000. Curr Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30182836 Review.
Cited by
-
Locally weighted histogram analysis and stochastic solution for large-scale multi-state free energy estimation.J Chem Phys. 2016 Jan 21;144(3):034107. doi: 10.1063/1.4939768. J Chem Phys. 2016. PMID: 26801020 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale asynchronous and distributed multidimensional replica exchange molecular simulations and efficiency analysis.J Comput Chem. 2015 Sep 5;36(23):1772-85. doi: 10.1002/jcc.23996. Epub 2015 Jul 7. J Comput Chem. 2015. PMID: 26149645 Free PMC article.
-
Asynchronous Replica Exchange Software for Grid and Heterogeneous Computing.Comput Phys Commun. 2015 Nov;196:236-246. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2015.06.010. Comput Phys Commun. 2015. PMID: 27103749 Free PMC article.
-
Simulating Replica Exchange: Markov State Models, Proposal Schemes, and the Infinite Swapping Limit.J Phys Chem B. 2016 Aug 25;120(33):8289-301. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.6b02015. Epub 2016 Apr 29. J Phys Chem B. 2016. PMID: 27079355 Free PMC article.
-
Free Energy-Based Virtual Screening and Optimization of RNase H Inhibitors of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase.ACS Omega. 2016 Sep 30;1(3):435-447. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.6b00123. Epub 2016 Sep 21. ACS Omega. 2016. PMID: 27713931 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

