Identification of genes encoding granule-bound starch synthase involved in amylose metabolism in banana fruit
- PMID: 24505384
- PMCID: PMC3913707
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088077
Identification of genes encoding granule-bound starch synthase involved in amylose metabolism in banana fruit
Abstract
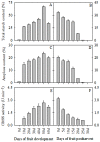
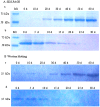
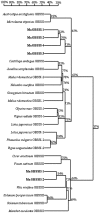
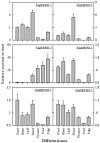
Granule-bound starch synthase (GBSS) is responsible for amylose synthesis, but the role of GBSS genes and their encoded proteins remains poorly understood in banana. In this study, amylose content and GBSS activity gradually increased during development of the banana fruit, and decreased during storage of the mature fruit. GBSS protein in banana starch granules was approximately 55.0 kDa. The protein was up-regulated expression during development while it was down-regulated expression during storage. Six genes, designated as MaGBSSI-1, MaGBSSI-2, MaGBSSI-3, MaGBSSI-4, MaGBSSII-1, and MaGBSSII-2, were cloned and characterized from banana fruit. Among the six genes, the expression pattern of MaGBSSI-3 was the most consistent with the changes in amylose content, GBSS enzyme activity, GBSS protein levels, and the quantity or size of starch granules in banana fruit. These results suggest that MaGBSSI-3 might regulate amylose metabolism by affecting the variation of GBSS levels and the quantity or size of starch granules in banana fruit during development or storage.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Natural Polymorphisms in Arabidopsis Result in Wide Variation or Loss of the Amylose Component of Starch.Plant Physiol. 2020 Feb;182(2):870-881. doi: 10.1104/pp.19.01062. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Plant Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31694903 Free PMC article.
-
Field evaluation of transgenic potato plants expressing an antisense granule-bound starch synthase gene: increase of the antisense effect during tuber growth.Plant Mol Biol. 1994 Dec;26(6):1759-73. doi: 10.1007/BF00019490. Plant Mol Biol. 1994. PMID: 7532028
-
PROTEIN TARGETING TO STARCH is required for localising GRANULE-BOUND STARCH SYNTHASE to starch granules and for normal amylose synthesis in Arabidopsis.PLoS Biol. 2015 Feb 24;13(2):e1002080. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002080. eCollection 2015 Feb. PLoS Biol. 2015. PMID: 25710501 Free PMC article.
-
Granule-bound starch synthase in plants: Towards an understanding of their evolution, regulatory mechanisms, applications, and perspectives.Plant Sci. 2023 Nov;336:111843. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2023.111843. Epub 2023 Aug 28. Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37648115 Review.
-
Posttranslational Modification of Waxy to Genetically Improve Starch Quality in Rice Grain.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 3;22(9):4845. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094845. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34063649 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular evolution accompanying functional divergence of duplicated genes along the plant starch biosynthesis pathway.BMC Evol Biol. 2014 May 15;14:103. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-14-103. BMC Evol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24884572 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular identification of the key starch branching enzyme-encoding gene SBE2.3 and its interacting transcription factors in banana fruits.Hortic Res. 2020 Jul 1;7:101. doi: 10.1038/s41438-020-0325-1. eCollection 2020. Hortic Res. 2020. PMID: 32637129 Free PMC article.
-
Lineage-Specific Evolutionary Histories and Regulation of Major Starch Metabolism Genes during Banana Ripening.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Dec 2;7:1778. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01778. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27994606 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characteristics and Functional Identification of a Key Alpha-Amylase-Encoding Gene AMY11 in Musa acuminata.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 17;25(14):7832. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147832. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063074 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive RNA-Seq-based gene expression atlas of the summer squash (Cucurbita pepo) provides insights into fruit morphology and ripening mechanisms.BMC Genomics. 2021 May 12;22(1):341. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07683-2. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33980145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Juansang J, Puttanlek C, Rungsardthong V, Puncha-arnon S, Uttapap D (2012) Effect of gelatinisation on slowly digestible starch and resistant starch of heat-moisture treated and chemically modified canna starches. Food Chem 131: 500–507.
-
- Liu J, Wen Y, Dong N, Lai C, Zhao G (2013) Authentication of lotus root powder adulterated with potato starch and/or sweet potato starch using fourier transform mid-infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem 141: 3103–3109. - PubMed
-
- Zeeman SC, Kossmann J, Smith AM (2010) Starch: Its metabolism, evolution, and biotechnological modification in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61: 209–234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

