Phosphorylation of mutant huntingtin at serine 116 modulates neuronal toxicity
- PMID: 24505464
- PMCID: PMC3914950
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088284
Phosphorylation of mutant huntingtin at serine 116 modulates neuronal toxicity
Abstract
Phosphorylation has been shown to have a significant impact on expanded huntingtin-mediated cellular toxicity. Several phosphorylation sites have been identified on the huntingtin (Htt) protein. To find new potential therapeutic targets for Huntington's Disease (HD), we used mass spectrometry to identify novel phosphorylation sites on N-terminal Htt, expressed in HEK293 cells. Using site-directed mutagenesis we introduced alterations of phosphorylation sites in a N586 Htt construct containing 82 polyglutamine repeats. The effects of these alterations on expanded Htt toxicity were evaluated in primary neurons using a nuclear condensation assay and a direct time-lapse imaging of neuronal death. As a result of these studies, we identified several novel phosphorylation sites, validated several known sites, and discovered one phospho-null alteration, S116A, that had a protective effect against expanded polyglutamine-mediated cellular toxicity. The results suggest that S116 is a potential therapeutic target, and indicate that our screening method is useful for identifying candidate phosphorylation sites.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

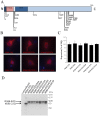
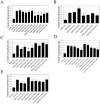

References
-
- Ross CA, Tabrizi SJ (2011) Huntington's disease: from molecular pathogenesis to clinical treatment. Lancet Neurol 10: 83–98. - PubMed
-
- Gusella JF, MacDonald ME (2006) Huntington's disease: seeing the pathogenic process through a genetic lens. Trends Biochem Sci 31: 533–540. - PubMed
-
- MacDonald ME (2003) Huntingtin: alive and well and working in middle management. Sci STKE 2003: pe48. - PubMed
-
- Walker FO (2007) Huntington's Disease. Semin Neurol 27: 143–150. - PubMed
-
- Imarisio S, Carmichael J, Korolchuk V, Chen CW, Saiki S, et al. (2008) Huntington's disease: from pathology and genetics to potential therapies. Biochem J 412: 191–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

