Secondary Myelodysplastic Syndrome May Happen Same as Paraneoplastic Syndrome in a Period of Time and Prior to The Appearance of Malignancy: A case Study of 6 Patients
- PMID: 24505525
- PMCID: PMC3913137
Secondary Myelodysplastic Syndrome May Happen Same as Paraneoplastic Syndrome in a Period of Time and Prior to The Appearance of Malignancy: A case Study of 6 Patients
Abstract
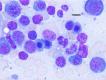
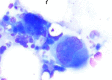
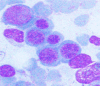
Myelodysplastic syndrome is a bone marrow failure in which differentiation and maturity do not happen naturally and dysplasia exists in each of 3 cell categories in Bone marrow. Refractory anemia is one of the major complaints with which the patients come to hematology clinics, which in diagnostic considerations lead to MDS as diagnosis. Often there is no recognized reason for this, so it is called "primary MDS". In practice, we meet some patients who have MDS criteria however we can also find specific reasons for it; therefore we call it "secondary MDS". One of the most important reasons for secondary MDS is the side effects of medications used in chemotherapy and radiotherapy in patients who undergo these therapies. We observed 6 patients in this case study during lengthy follow up that were diagnosed as MDS and during follow up period malignancy appeared in 6 cases. Supportive and therapeutic measures in these patients did not considerably improve blood cell count, most patients required blood injection and antibiotics for infection treatment. However align with malignancy treatment such problems are completely resolved both in terms of clinical and laboratory.
Keywords: Malignancy; Myelodysplastic syndrome; Paraneoplastic syndrome.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Physician Education: Myelodysplastic Syndrome.Oncologist. 1996;1(4):284-287. Oncologist. 1996. PMID: 10388004
-
[Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Aspects of hematopathologic diagnosis].Pathologe. 2000 Jan;21(1):1-15. doi: 10.1007/s002920050001. Pathologe. 2000. PMID: 10663664 Review. German.
-
Measurement of secondary colony formation after 5 weeks in long-term cultures in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome.Leukemia. 1998 Aug;12(8):1187-94. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2401084. Leukemia. 1998. PMID: 9697872
-
Myelodysplastic syndrome in children: differentiation from acute myeloid leukemia with a low blast count.Leukemia. 1997 Feb;11(2):206-11. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2400558. Leukemia. 1997. PMID: 9009082 Review.
-
The Pulmonary Complications of Paraneoplastic Autoimmune Vasculitis in a Patient With Myelodysplastic Syndrome.Cureus. 2020 Jul 19;12(7):e9282. doi: 10.7759/cureus.9282. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 32821625 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Greenberg PL. The smoldering myeloid leukemia states: clinical and biologic features. Blood. 1983;61:1035–1044. - PubMed
-
- Koeffler HP, Golde DW. Human preleukemia. Ann Intern Med. 1980;93:347–353. - PubMed
-
- Noel P, Solberg LA., Jr Myelodysplastic syndromes. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1992;12:193–215. - PubMed
-
- Williamson PJ, Kruger AR, Reynolds PJ, et al. Establishing the incidence of myelodysplastic syndrome. Br J Haematol. 1994;87:743–745. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
