Contour-driven regression for label inference in atlas-based segmentation
- PMID: 24505763
- PMCID: PMC3935362
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-40760-4_27
Contour-driven regression for label inference in atlas-based segmentation
Abstract
We present a novel method for inferring tissue labels in atlas-based image segmentation using Gaussian process regression. Atlas-based segmentation results in probabilistic label maps that serve as input to our method. We introduce a contour-driven prior distribution over label maps to incorporate image features of the input scan into the label inference problem. The mean function of the Gaussian process posterior distribution yields the MAP estimate of the label map and is used in the subsequent voting. We demonstrate improved segmentation accuracy when our approach is combined with two different patch-based segmentation techniques. We focus on the segmentation of parotid glands in CT scans of patients with head and neck cancer, which is important for radiation therapy planning.
Figures

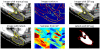
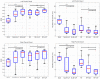
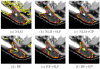
Similar articles
-
Atlas-based auto-segmentation of head and neck CT images.Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2008;11(Pt 2):434-41. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-85990-1_52. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2008. PMID: 18982634
-
Supervised probabilistic segmentation of pulmonary nodules in CT scans.Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2006;9(Pt 2):912-9. doi: 10.1007/11866763_112. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2006. PMID: 17354860
-
Segmentation of neck lymph nodes in CT datasets with stable 3D mass-spring models segmentation of neck lymph nodes.Acad Radiol. 2007 Nov;14(11):1389-99. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2007.09.001. Acad Radiol. 2007. PMID: 17964462
-
Interactive semiautomatic contour delineation using statistical conditional random fields framework.Med Phys. 2012 Jul;39(7):4547-58. doi: 10.1118/1.4728979. Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 22830786 Free PMC article.
-
Automated delineation of radiotherapy volumes: are we going in the right direction?Br J Radiol. 2013 Jan;86(1021):20110718. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20110718. Br J Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23239689 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Contour-Driven Atlas-Based Segmentation.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2015 Dec;34(12):2492-505. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2015.2442753. Epub 2015 Jun 9. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2015. PMID: 26068202 Free PMC article.
-
Vision 20/20: perspectives on automated image segmentation for radiotherapy.Med Phys. 2014 May;41(5):050902. doi: 10.1118/1.4871620. Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 24784366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atlas-based under-segmentation.Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2014;17(Pt 1):315-22. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10404-1_40. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2014. PMID: 25333133 Free PMC article.
-
Globally Optimal Label Fusion with Shape Priors.Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2016 Oct;9901:538-546. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46723-8_62. Epub 2016 Oct 2. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2016. PMID: 28626843 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic segmentation of head and neck CT images for radiotherapy treatment planning using multiple atlases, statistical appearance models, and geodesic active contours.Med Phys. 2014 May;41(5):051910. doi: 10.1118/1.4871623. Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 24784389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arbelaez P, Maire M, Fowlkes C, Malik J. Contour detection and hierarchical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. on Pat. Anal. Mach. Intel. 2011;33(5):898–916. - PubMed
-
- Breiman L. Random forests. Machine Learning. 2001;45(1):5–32.
-
- Chen A, Noble JH, Niermann KJ, Deeley MA, Dawant BM. Segmentation of parotid glands in head and neck CT images using a constrained active shape model with landmark uncertainty. SPIE. 2012;vol. 8314:83140P.
-
- Coupé P, Manjón JV, Fonov V, Pruessner J, Robles M, Collins DL. Patch-based segmentation using expert priors: Application to hippocampus and ventricle segmentation. NeuroImage. 2011;54(2):940–954. - PubMed
-
- Han X, Hibbard LS, O'connell NP, Willcut V. Medical Image Analysis for the Clinic: A Grand Challenge. 2010. Automatic segmentation of parotids in head and neck CT images using multi-atlas fusion; pp. 297–304.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
