The survival times of malaria-infected mice are prolonged more by several new two-carbon-linked artemisinin-derived dimer carbamates than by the trioxane antimalarial drug artemether
- PMID: 24508128
- PMCID: PMC3943161
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.01.059
The survival times of malaria-infected mice are prolonged more by several new two-carbon-linked artemisinin-derived dimer carbamates than by the trioxane antimalarial drug artemether
Abstract
Sixteen new artemisinin-derived 2-carbon-linked trioxane dimers were prepared to study chemical structure/antimalarial activity relationships (SAR). Administering a very low single oral dose of only 5mg/kg of dimer secondary alcohol 6a or 6b plus 15 mg/kg of mefloquine hydrochloride prolonged the lives of Plasmodium berghei-infected mice to an average of 25 days after infection. This ACT chemotherapy result is of high medicinal significance because the antimalarial efficacy of the popular trioxane drug artemether (2) plus mefloquine under the same conditions was significantly lower (only 20 day average survival). NH-aryl carbamate derivatives 7e, 7i, and 7j of 2-carbon-linked dimer alcohol 6b also significantly outperformed artemether (2) in prolonging the survival times (25-27 days) of malaria-infected mice.
Keywords: Antimalarial chemotherapy; Oral bioavailability; Single oral dose ACT; Trioxane dimer carbamates.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


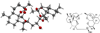

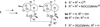

Similar articles
-
Antimalarial chemotherapy: artemisinin-derived dimer carbonates and thiocarbonates.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014 Jun 1;24(11):2440-3. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.04.025. Epub 2014 Apr 16. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014. PMID: 24775306 Free PMC article.
-
Antimalarial chemotherapy: orally curative artemisinin-derived trioxane dimer esters.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Jan 15;25(2):245-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.11.064. Epub 2014 Nov 27. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015. PMID: 25481079 Free PMC article.
-
A single, low, oral dose of a 5-carbon-linked trioxane dimer orthoester plus mefloquine cures malaria-infected mice.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011 May 1;21(9):2773-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.09.123. Epub 2010 Sep 29. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011. PMID: 20952197 Free PMC article.
-
[Combined antimalarial therapy using artemisinin].Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):85-7. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305693 Review. Italian.
-
Considerations on the mechanism of action of artemisinin antimalarials: part 1--the 'carbon radical' and 'heme' hypotheses.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2013 Aug;13(4):217-77. doi: 10.2174/1871526513666131129155708. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2013. PMID: 24304352 Review.
Cited by
-
Antimalarial chemotherapy: artemisinin-derived dimer carbonates and thiocarbonates.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014 Jun 1;24(11):2440-3. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.04.025. Epub 2014 Apr 16. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014. PMID: 24775306 Free PMC article.
-
Antimalarial chemotherapy: orally curative artemisinin-derived trioxane dimer esters.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Jan 15;25(2):245-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.11.064. Epub 2014 Nov 27. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015. PMID: 25481079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The RTS. S Clinical Trials Partnership. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011;365:1863. - PubMed
-
- Olliaro PL, Boland PB. In: Antimalarial Chemotherapy: Mechanisms of Action, Resistance, and New Directions in Drug Discovery. Rosenthal PJ, editor. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press; 2001. pp. 65–84. - PubMed
-
- Schlitzer M. ChemMed Chem. 2007;2:955.
-
- Slack RD, Jacobine AM, Posner GH. Med. Chem. Commun. 2012;3:281.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

