Ly108 expression distinguishes subsets of invariant NKT cells that help autoantibody production and secrete IL-21 from those that secrete IL-17 in lupus prone NZB/W mice
- PMID: 24508410
- PMCID: PMC4002579
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2014.01.002
Ly108 expression distinguishes subsets of invariant NKT cells that help autoantibody production and secrete IL-21 from those that secrete IL-17 in lupus prone NZB/W mice
Abstract
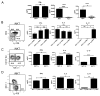
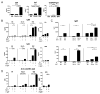
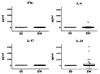
Lupus is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by anti-nuclear antibodies in humans and genetically susceptible NZB/W mice that can cause immune complex glomerulonephritis. T cells contribute to lupus pathogenesis by secreting pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-17, and by interacting with B cells and secreting helper factors such as IL-21 that promote production of IgG autoantibodies. In the current study, we determined whether purified NKT cells or far more numerous conventional non-NKT cells in the spleen of NZB/W female mice secrete IL-17 and/or IL-21 after TCR activation in vitro, and provide help for spontaneous IgG autoantibody production by purified splenic CD19(+) B cells. Whereas invariant NKT cells secreted large amounts of IL-17 and IL-21, and helped B cells, non-NKT cells did not. The subset of IL-17 secreting NZB/W NKT cells expressed the Ly108(lo)CD4(-)NK1.1(-) phenotype, whereas the IL-21 secreting subset expressed the Ly108(hi)CD4(+)NK1.1(-) phenotype and helped B cells secrete a variety of IgG anti-nuclear antibodies. α-galactocylceramide enhanced the helper activity of NZB/W and B6.Sle1b NKT cells for IgG autoantibody secretion by syngeneic B cells. In conclusion, different subsets of iNKT cells from mice with genetic susceptibility to lupus can contribute to pathogenesis by secreting pro-inflammatory cytokines and helping autoantibody production.
Keywords: Autoantibodies; IL-17; IL-21; Natural killer T cells; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


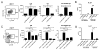
Similar articles
-
Natural killer T cells and innate immune B cells from lupus-prone NZB/W mice interact to generate IgM and IgG autoantibodies.Eur J Immunol. 2008 Jan;38(1):156-65. doi: 10.1002/eji.200737656. Eur J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18050273 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-galactosylceramide alters invariant natural killer T cell function and is effective treatment for lupus.Clin Immunol. 2009 Sep;132(3):321-33. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2009.05.018. Epub 2009 Jun 28. Clin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19564135 Free PMC article.
-
Invariant natural killer T cells in lupus patients promote IgG and IgG autoantibody production.Eur J Immunol. 2015 Feb;45(2):612-23. doi: 10.1002/eji.201444760. Epub 2014 Nov 27. Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25352488 Free PMC article.
-
Role of invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells in systemic lupus erythematosus.Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(18):1778-87. doi: 10.2174/092986708785132988. Curr Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18691038 Review.
-
Immunoregulation of NKT Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:206731. doi: 10.1155/2015/206731. Epub 2015 Dec 24. J Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 26819956 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neural Regeneration in Dry Eye Secondary to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Is Also Disrupted like in Rheumatoid Arthritis, but in a Progressive Fashion.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 26;24(13):10680. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310680. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445856 Free PMC article.
-
What rheumatologists need to know about innate lymphocytes.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016 Nov;12(11):658-668. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.140. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 27586381 Review.
-
The Janus Face of NKT Cell Function in Autoimmunity and Infectious Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 1;19(2):440. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020440. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29389901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repeated administration of alpha-galactosylceramide ameliorates experimental lupus nephritis in mice.Sci Rep. 2018 May 29;8(1):8225. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26470-w. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29844470 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Jo-1 Autoantibody and Isolated Arthritis in the Antisynthetase Syndrome: Review of the Literature and Report of the Experience of AENEAS Collaborative Group.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017 Feb;52(1):71-80. doi: 10.1007/s12016-016-8528-9. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017. PMID: 26782036 Review.
References
-
- Kotzin BL. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell. 1996;85:303–6. - PubMed
-
- Theofilopoulos AN, Kofler R, Singer PA, Dixon FJ. Molecular genetics of murine lupus models. Adv Immunol. 1989;46:61–109. - PubMed
-
- Tsokos GC. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:2110–21. - PubMed
-
- Ando DG, Sercarz EE, Hahn BH. Mechanisms of T and B cell collaboration in the in vitro production of anti-DNA antibodies in the NZB/NZW F1 murine SLE model. J Immunol. 1987;138:3185–90. - PubMed
-
- Borchers A, Ansari AA, Hsu T, Kono DH, Gershwin ME. The pathogenesis of autoimmunity in New Zealand mice. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2000;29:385–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

