Development of high efficiency ventilation bag actuated dry powder inhalers
- PMID: 24508552
- PMCID: PMC4051231
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.01.043
Development of high efficiency ventilation bag actuated dry powder inhalers
Abstract
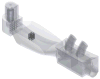
New active dry powder inhaler systems were developed and tested to efficiently aerosolize a carrier-free formulation. To assess inhaler performance, a challenging case study of aerosol lung delivery during high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) therapy was selected. The active delivery system consisted of a ventilation bag for actuating the device, the DPI containing a flow control orifice and 3D rod array, and streamlined nasal cannula with separate inlets for the aerosol and HFNC therapy gas. In vitro experiments were conducted to assess deposition in the device, emitted dose (ED) from the nasal cannula, and powder deaggregation. The best performing systems achieved EDs of 70-80% with fine particle fractions <5 μm of 65-85% and mass median aerodynamic diameters of 1.5 μm, which were target conditions for controlled condensational growth aerosol delivery. Decreasing the size of the flow control orifice from 3.6 to 2.3mm reduced the flow rate through the system with manual bag actuations from an average of 35 to 15LPM, while improving ED and aerosolization performance. The new devices can be applied to improve aerosol delivery during mechanical ventilation, nose-to-lung aerosol administration, and to assist patients that cannot reproducibly use passive DPIs.
Keywords: Active dry power inhaler (DPI); Excipient enhanced growth (EEG) formulation; High efficiency DPI; Noninvasive ventilation; Nose to lung aerosol delivery; Streamlined ventilation components.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


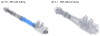

References
-
- Ari A, Fink JB. Inhalation therapy in patients receiving mechanical ventilation: an update. Journal of Aerosol Medicine and Pulmonary Drug Delivery. 2012;25:319–332. - PubMed
-
- Ari A, Harwood R, Sheard M, Dailey P, Fink JB. In vitro comparison of heliox and oxygen in aerosol delivery using pediatric high flow nasal cannula. Pediatric Pulmonology. 2011;46:795–801. - PubMed
-
- Bhashyam AR, Wolf MT, Marcinkowski AL, Saville A, Thomas K, Carcillo JA, Corcoran TE. Aerosol delivery through nasal cannulas: An in vitro study. Journal of Aerosol Medicine and Pulmonary Drug Delivery. 2008;21:181–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

