A semi-automated method for purification of milligram quantities of proteins on the QIAcube
- PMID: 24508590
- PMCID: PMC4287359
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pep.2014.01.014
A semi-automated method for purification of milligram quantities of proteins on the QIAcube
Abstract
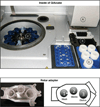
A growing number of studies require the purification of multiple proteins simultaneously and the development of simple economical high-throughput purification methods is essential. We have tested the purification of two related proteins in a variety of conditions to benchmark the semi-automated affinity chromatography method for the QIAcube that we have developed. We find that this new QIAcube method can successfully purify milligram quantities of proteins with minimal user involvement and performs as well as methods based on gravity. The method could easily be adapted to other chromatography resins and should prove to be a versatile method for optimizing protein expression or purification conditions for multiple proteins while obtaining sufficient amounts for subsequent biochemical analyses.
Keywords: High-throughput automation; Protein expression; Protein purification; QIAcube; SH3 domain.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
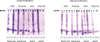
References
-
- Lin C-T, Moore P, Auberry D, Landorf E, Peppler T, Victry K, Collart F, Kery V. Automated purification of recombinant proteins: combining high-throughput with high yield. Protein expression and purification. 2006;47:16–24. - PubMed
-
- Braun P, LaBaer J. High throughput protein production for functional proteomics. Trends in biotechnology. 2003;21:383–388. - PubMed
-
- Lichty J, Malecki J, Agnew H, Michelson-Horowitz D, Tan S. Comparison of affinity tags for protein purification. Protein expression and purification. 2005;41:98–105. - PubMed
-
- Carapito R, Gallet B, Zapun A, Vernet T. Automated high-throughput process for site-directed mutagenesis, production, purification, and kinetic characterization of enzymes. Analytical biochemistry. 2006;355:110–116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

