Skeletal muscle hypertrophy after aerobic exercise training
- PMID: 24508740
- PMCID: PMC4523889
- DOI: 10.1249/JES.0000000000000007
Skeletal muscle hypertrophy after aerobic exercise training
Abstract
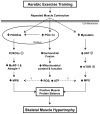
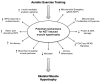
Current dogma suggests that aerobic exercise training has minimal effects on skeletal muscle size. We and others have demonstrated that aerobic exercise acutely and chronically alters protein metabolism and induces skeletal muscle hypertrophy. These findings promote an antithesis to the status quo by providing novel perspective on skeletal muscle mass regulation and insight into exercise countermeasures for populations prone to muscle loss.
Figures
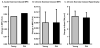
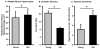
Similar articles
-
Aerobic exercise training induces skeletal muscle hypertrophy and age-dependent adaptations in myofiber function in young and older men.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012 Nov;113(9):1495-504. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00786.2012. Epub 2012 Sep 13. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012. PMID: 22984247 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Regulation of Exercise-Induced Muscle Fiber Hypertrophy.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018 Jun 1;8(6):a029751. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a029751. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018. PMID: 28490543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Markers of human skeletal muscle mitochondrial biogenesis and quality control: effects of age and aerobic exercise training.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2014 Apr;69(4):371-8. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glt107. Epub 2013 Jul 20. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 23873965 Free PMC article.
-
The Nuclear Receptor Nor-1 Is a Pleiotropic Regulator of Exercise-Induced Adaptations.Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2018 Apr;46(2):97-104. doi: 10.1249/JES.0000000000000143. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2018. PMID: 29346164 Review.
-
Interference between concurrent resistance and endurance exercise: molecular bases and the role of individual training variables.Sports Med. 2014 Jun;44(6):743-62. doi: 10.1007/s40279-014-0162-1. Sports Med. 2014. PMID: 24728927 Review.
Cited by
-
Cycle training modulates satellite cell and transcriptional responses to a bout of resistance exercise.Physiol Rep. 2016 Sep;4(18):e12973. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12973. Physiol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27650251 Free PMC article.
-
Physical Activity as the Best Supportive Care in Cancer: The Clinician's and the Researcher's Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 2;14(21):5402. doi: 10.3390/cancers14215402. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Questioning the Resistance/Aerobic Training Dichotomy: A commentary on physiological adaptations determined by effort rather than exercise modality.J Hum Kinet. 2014 Dec 30;44:137-42. doi: 10.2478/hukin-2014-0119. eCollection 2014 Dec 9. J Hum Kinet. 2014. PMID: 25713674 Free PMC article.
-
Comparisons of Resistance Training and "Cardio" Exercise Modalities as Countermeasures to Microgravity-Induced Physical Deconditioning: New Perspectives and Lessons Learned From Terrestrial Studies.Front Physiol. 2019 Sep 10;10:1150. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01150. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31551818 Free PMC article.
-
Role of exercise in age-related sarcopenia.J Exerc Rehabil. 2018 Aug 24;14(4):551-558. doi: 10.12965/jer.1836268.134. eCollection 2018 Aug. J Exerc Rehabil. 2018. PMID: 30276173 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Charifi N, Kadi F, Feasson L, Denis C. Effects of endurance training on satellite cell frequency in skeletal muscle of old men. Muscle & Nerve. 2003;28(1):87–92. - PubMed
-
- Coggan AR, Spina RJ, King DS, Rogers MA, Brown M, Nemeth PM, Holloszy JO. Histochemical and enzymatic comparison of the gastrocnemius muscle of young and elderly men and women. J Gerontol. 1992;47(3):B71–6. - PubMed
-
- Coggan AR, Spina RJ, King DS, Rogers MA, Brown M, Nemeth PM, Holloszy JO. Skeletal muscle adaptations to endurance training in 60- to 70-yr-old men and women. J Appl Physiol. 1992;72(5):1780–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

