A committed precursor to innate lymphoid cells
- PMID: 24509713
- PMCID: PMC4003507
- DOI: 10.1038/nature13047
A committed precursor to innate lymphoid cells
Abstract
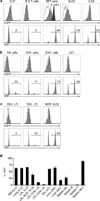
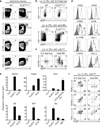
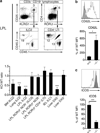
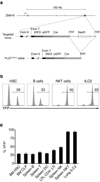
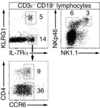
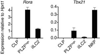
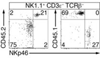
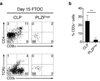
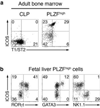
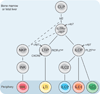
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) specialize in the rapid secretion of polarized sets of cytokines and chemokines to combat infection and promote tissue repair at mucosal barriers. Their diversity and similarities with previously characterized natural killer (NK) cells and lymphoid tissue inducers (LTi) have prompted a provisional classification of all innate lymphocytes into groups 1, 2 and 3 solely on the basis of cytokine properties, but their developmental pathways and lineage relationships remain elusive. Here we identify and characterize a novel subset of lymphoid precursors in mouse fetal liver and adult bone marrow that transiently express high amounts of PLZF, a transcription factor previously associated with NK T cell development, by using lineage tracing and transfer studies. PLZF(high) cells were committed ILC progenitors with multiple ILC1, ILC2 and ILC3 potential at the clonal level. They excluded classical LTi and NK cells, but included a peculiar subset of NK1.1(+)DX5(-) 'NK-like' cells residing in the liver. Deletion of PLZF markedly altered the development of several ILC subsets, but not LTi or NK cells. PLZF(high) precursors also expressed high amounts of ID2 and GATA3, as well as TOX, a known regulator of PLZF-independent NK and LTi lineages. These findings establish novel lineage relationships between ILC, NK and LTi cells, and identify the common precursor to ILCs, termed ILCP. They also reveal the broad, defining role of PLZF in the differentiation of innate lymphocytes.
Figures

References
-
- Moro K, et al. Innate production of T(H)2 cytokines by adipose tissue-associated c-Kit(+)Sca-1(+) lymphoid cells. Nature. 2010;463:540–544. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01HL118092/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007605/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- T32 GM007281/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007090/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI108643/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI038339/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000430/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI038339/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK42086/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK042086/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL118092/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

