Alterations in dysadherin expression and F-actin reorganization: a possible mechanism of hypericin-mediated photodynamic therapy in colon adenocarcinoma cells
- PMID: 24510318
- PMCID: PMC4329297
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-013-9688-6
Alterations in dysadherin expression and F-actin reorganization: a possible mechanism of hypericin-mediated photodynamic therapy in colon adenocarcinoma cells
Abstract
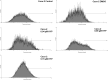
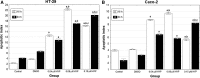
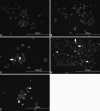
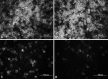
Dysadherin is a recently found anti-adhesion molecule, therefore detection and down regulation of its expression is promising in cancer treatment. The up-regulation of dysadherin contributes to colon cancer recurrence and metastasis. Dysadherin also has connections with cytoskeletal proteins and it can cause alterations in the organisation of filamentous actin (F-actin) in metastatic cancers. In this study, hypericin (HYP)-mediated photodynamic therapy (PDT) was performed in two different grade colon adenocarcinoma cell lines HT-29 (Grade I) and Caco-2 (Grade II). Cells were treated with 0.04, 0.08 or 0.15 μM HYP concentrations and irradiated with (4 J/cm(2)) fluorescent lamps. The effects of HYP was examined 16 and 24 h after the activation. We investigated for the first time the effect of HYP-mediated PDT on the expression of dysadherin and F-actin organisation. According to the results, HYP mediated PDT caused a decrease in gene expression and immunofluorescence staining of dysadherin and an increase in actin stress fibers and actin aggregates in HT-29 and Caco-2 cell lines. Besides, cytotoxicity, number of floating cells and apoptotic index changed depending on the cell type, HYP concentration and incubation time. We have demonstrated for the first time that dysadherin and F-actin could be target molecules for HYP-mediated PDT in HT-29 and Caco-2 colon cancer cell lines.
Figures














Similar articles
-
An Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spin labeling study in HT-29 Colon adenocarcinoma cells after Hypericin-mediated photodynamic therapy.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Jun 20;20(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12860-019-0205-4. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31221093 Free PMC article.
-
Response surface method optimization of a novel Hypericin formulation in P123 micelles for colorectal cancer and antimicrobial photodynamic therapy.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2017 May;170:247-255. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.04.008. Epub 2017 Apr 12. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2017. PMID: 28454049
-
Hypericin-mediated photodynamic therapy inhibits growth of colorectal cancer cells via inducing S phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 5;900:174071. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174071. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33811836
-
Hypericin in the Dark: Foe or Ally in Photodynamic Therapy?Cancers (Basel). 2016 Oct 14;8(10):93. doi: 10.3390/cancers8100093. Cancers (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27754424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysadherin: a new player in cancer progression.Cancer Lett. 2007 Oct 8;255(2):161-9. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2007.02.018. Epub 2007 Apr 17. Cancer Lett. 2007. PMID: 17442482 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ARID1A knockdown enhances carcinogenesis features and aggressiveness of Caco-2 colon cancer cells: An in vitro cellular mechanism study.J Cancer. 2022 Jan 1;13(2):373-384. doi: 10.7150/jca.65511. eCollection 2022. J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35069887 Free PMC article.
-
An Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spin labeling study in HT-29 Colon adenocarcinoma cells after Hypericin-mediated photodynamic therapy.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Jun 20;20(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12860-019-0205-4. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31221093 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotoxic Effect of Fipronil in Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cell Line.Neurotox Res. 2020 Jan;37(1):30-40. doi: 10.1007/s12640-019-00093-z. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Neurotox Res. 2020. PMID: 31482323
-
The Remodulation of Actin Bundles during the Stimulation of Mitochondria in Adult Human Fibroblasts in Response to Light.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Dec 22;16(1):20. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16010020. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38258031 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

