Sex differences in quality of life after ischemic stroke
- PMID: 24510493
- PMCID: PMC4211921
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000208
Sex differences in quality of life after ischemic stroke
Abstract
Objective: We aimed to compare quality of life (QOL) in women and men after ischemic stroke or TIA, and to determine the incremental impact of demographic, socioeconomic, clinical, and stroke-specific effects on longitudinal QOL.
Methods: We assessed QOL in patients with ischemic stroke or TIA at 3 and 12 months postdischarge in the Adherence eValuation After Ischemic stroke-Longitudinal Registry using the European Quality of Life-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D) instrument. We generated multivariable linear regression models to evaluate the association between sex and EQ-5D while sequentially adjusting for sociodemographic, clinical, and stroke-related variables. We also used a proportional odds model to assess sex differences in the change in EQ-5D scores from 3 to 12 months.
Results: A total of 1,370 patients were included, 53.7% male, median age 65 years (interquartile range 56-77 years). Women had significantly lower QOL at 3 months (unadjusted EQ-5D 0.81 in women vs 0.84 in men; p < 0.001) and 12 months (0.83 vs men 0.84; p < 0.001) poststroke. After multivariable adjustment for sociodemographic, clinical, and stroke-related factors, women continued to have lower QOL at 3 months (mean difference -0.036; p = 0.003) and at 12 months (mean difference -0.022; p = 0.046). Women fared worse in the dimensions of mobility, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/depression at 3 and 12 months. There were no sex differences in change in EQ-5D score from 3 to 12 months.
Conclusion: Women have worse QOL than men up to 12 months after stroke, even after adjusting for important sociodemographic variables, stroke severity, and disability.
Figures
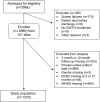

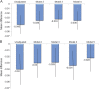
Comment in
-
Comment: Does patient sex affect decision-making after hemorrhagic stroke?Neurology. 2017 Jul 25;89(4):353. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004162. Epub 2017 Jun 28. Neurology. 2017. PMID: 28659420 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sturm JW, Donnan GA, Dewey HM, et al. . Quality of life after stroke: the North East Melbourne Stroke Incidence Study (NEMESIS). Stroke 2004;35:2340–2345 - PubMed
-
- Patel MD, McKevitt C, Lawrence E, Rudd AG, Wolfe CD. Clinical determinants of long-term quality of life after stroke. Age Ageing 2007;36:316–322 - PubMed
-
- Delcourt C, Hackett M, Wu Y, et al. . Determinants of quality of life after stroke in China: the ChinaQUEST (QUality Evaluation of Stroke care and Treatment) Study. Stroke 2011;42:433–438 - PubMed
-
- Gargano JW, Reeves MJ. Sex differences in stroke recovery and stroke-specific quality of life: results from a statewide stroke registry. Stroke 2007;38:2541–2548 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
