TGF-β: duality of function between tumor prevention and carcinogenesis
- PMID: 24511106
- PMCID: PMC3952197
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djt369
TGF-β: duality of function between tumor prevention and carcinogenesis
Abstract
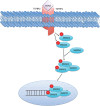
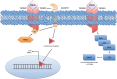
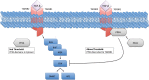
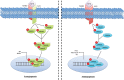
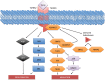
Several mechanisms underlying tumor progression have remained elusive, particularly in relation to transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β). Although TGF-β initially inhibits epithelial growth, it appears to promote the progression of advanced tumors. Defects in normal TGF-β pathways partially explain this paradox, which can lead to a cascade of downstream events that drive multiple oncogenic pathways, manifesting as several key features of tumorigenesis (uncontrolled proliferation, loss of apoptosis, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, sustained angiogenesis, evasion of immune surveillance, and metastasis). Understanding the mechanisms of TGF-β dysregulation will likely reveal novel points of convergence between TGF-β and other pathways that can be specifically targeted for therapy.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

