Angiopoietin-2-induced arterial stiffness in CKD
- PMID: 24511140
- PMCID: PMC4033368
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2013050542
Angiopoietin-2-induced arterial stiffness in CKD
Abstract
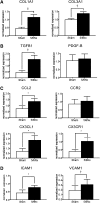
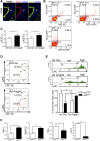
The mechanism of vascular calcification in CKD is not understood fully, but may involve collagen deposition in the arterial wall upon osteo/chondrocytic transformation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). Increased levels of circulating angiopoietin-2 correlate with markers of CKD progression and angiopoietin-2 regulate inflammatory responses, including intercellular and vascular adhesion and recruitment of VSMCs. Here, we investigate the potential role of angiopoietin-2 in the pathogenesis of arterial stiffness associated with CKD. In a cohort of 416 patients with CKD, the plasma level of angiopoietin-2 correlated independently with the severity of arterial stiffness assessed by pulse wave velocity. In mice subjected to 5/6 subtotal nephrectomy or unilateral ureteral obstruction, plasma levels of angiopoietin-2 also increased. Angiopoietin-2 expression markedly increased in tubular epithelial cells of fibrotic kidneys but decreased in other tissues, including aorta and lung, after 5/6 subtotal nephrectomy. Expression of collagen and profibrotic genes in aortic VSMCs increased in mice after 5/6 subtotal nephrectomy and in mice producing human angiopoietin-2. Angiopoietin-2 stimulated endothelial expression of chemokines and adhesion molecules for monocytes, increased Ly6C(low) macrophages in aorta, and increased the expression of the profibrotic cytokine TGF-β1 in aortic endothelial cells and Ly6C(low) macrophages. Angiopoietin-2 blockade attenuated expression of monocyte chemokines, profibrotic cytokines, and collagen in aorta of mice after 5/6 subtotal nephrectomy. This study identifies angiopoietin-2 as a link between kidney fibrosis and arterial stiffness. Targeting angiopoietin-2 to attenuate inflammation and collagen expression may provide a novel therapy for cardiovascular disease in CKD.
Copyright © 2014 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures






References
-
- Levin A, Foley RN: Cardiovascular disease in chronic renal insufficiency. Am J Kidney Dis 36[Suppl 3]: S24–S30, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Foley RN, Murray AM, Li S, Herzog CA, McBean AM, Eggers PW, Collins AJ: Chronic kidney disease and the risk for cardiovascular disease, renal replacement, and death in the United States Medicare population, 1998 to 1999. J Am Soc Nephrol 16: 489–495, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Park M, Hsu CY, Li Y, Mishra RK, Keane M, Rosas SE, Dries D, Xie D, Chen J, He J, Anderson A, Go AS, Shlipak MG, Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study Group : Associations between kidney function and subclinical cardiac abnormalities in CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol 23: 1725–1734, 2012 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Guerin AP, Blacher J, Pannier B, Marchais SJ, Safar ME, London GM: Impact of aortic stiffness attenuation on survival of patients in end-stage renal failure. Circulation 103: 987–992, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

