Nanoparticles for multimodal in vivo imaging in nanomedicine
- PMID: 24511229
- PMCID: PMC3915020
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S53717
Nanoparticles for multimodal in vivo imaging in nanomedicine
Abstract
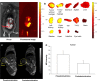
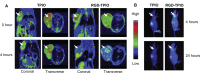
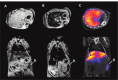
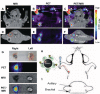
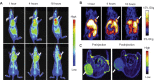
While nanoparticles are usually designed for targeted drug delivery, they can also simultaneously provide diagnostic information by a variety of in vivo imaging methods. These diagnostic capabilities make use of specific properties of nanoparticle core materials. Near-infrared fluorescent probes provide optical detection of cells targeted by real-time nanoparticle-distribution studies within the organ compartments of live, anesthetized animals. By combining different imaging modalities, we can start with deep-body imaging by magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography, and by using optical imaging, get down to the resolution required for real-time fluorescence-guided surgery.
Keywords: CT; MRI; NIRF; PET; cancer; multimodal imaging; nanomedicine; nanoparticles.
Figures


References
-
- van Dam GM, Themelis G, Crane LM, et al. Intraoperative tumor-specific fluorescence imaging in ovarian cancer by folate receptor-α targeting: first in-human results. Nat Med. 2011;17(10):1315–1319. - PubMed
-
- Leary JF. Nanotechnology: what is it and why is small so big? Can J Ophthalmol. 2010;45(5):449–456. - PubMed
-
- Hahn M, Singh A, Sharma P, Brown S, Moudgil B. Nanoparticles as contrast agents for in vivo bioimaging: current status and future perspectives. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011;399(1):3–27. - PubMed
-
- Cheon J, Lee JH. Synergistically integrated nanoparticles as multimodal probes for nanobiotechnology. Acc Chem Res. 2008;41(12):1630–1640. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

