Aromatic-aromatic interactions enhance interfiber contacts for enzymatic formation of a spontaneously aligned supramolecular hydrogel
- PMID: 24512553
- PMCID: PMC3986011
- DOI: 10.1021/ja4127399
Aromatic-aromatic interactions enhance interfiber contacts for enzymatic formation of a spontaneously aligned supramolecular hydrogel
Abstract
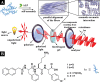
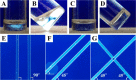
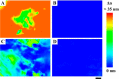
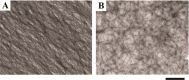
Anisotropy or alignment is a critical feature of functional soft materials in living organisms, but it remains a challenge for spontaneously generating anisotropic gel materials. Here we report a molecular design that increases intermolecular aromatic-aromatic interactions of hydrogelators during enzymatic hydrogelation for spontaneously forming an anisotropic hydrogel. This process, relying on both aromatic-aromatic interactions and enzyme catalysis, results in spontaneously aligned supramolecular nanofibers as the matrices of a monodomain hydrogel that exhibits significant birefringence. This work, as the first example of monodomain hydrogels formed via an enzymatic reaction, illustrates a new biomimetic approach for generating aligned anisotropic soft materials.
Figures

References
-
- Gray G. W. Liq. Cryst. 1998, 24, 5.
-
- Cox J. R.; Simpson J. H.; Swager T. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 640. - PubMed
- Hoogboom J.; Swager T. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 15058. - PubMed
- Kato T.; Yasuda T.; Kamikawa Y.; Yoshio M. Chem. Commun. 2009, 729. - PubMed
- Kato T.; Mizoshita N.; Kanie K. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2001, 22, 797.
-
- Zhang S. M.; Greenfield M. A.; Mata A.; Palmer L. C.; Bitton R.; Mantei J. R.; Aparicio C.; de la Cruz M. O.; Stupp S. I. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 594. - PMC - PubMed
- Wu Z. L.; Kurokawa T.; Liang S.; Furukawa H.; Gong J. P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10064. - PubMed
- Zhao F.; Gao Y. A.; Shi J. F.; Browdy H. M.; Xu B. Langmuir 2011, 27, 1510. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

