Invariant NKT cells provide innate and adaptive help for B cells
- PMID: 24514004
- PMCID: PMC4346131
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2014.01.007
Invariant NKT cells provide innate and adaptive help for B cells
Abstract
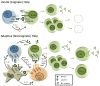
B cells rely on CD4(+) T cells helper signals to optimize their responses to T-dependent antigens. Recently another subset of T cells has been identified which provides help for B cells, invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells. iNKT cells are unique because they provide both innate and adaptive forms of help to B cells, with divergent outcomes. iNKT cells are widely distributed throughout the spleen at rest, consolidate in the marginal zone of the spleen early after activation, and are later found in germinal centers. Understanding the activation requirements for iNKT cells has led to the development of glycolipid containing nanoparticles which efficiently activate iNKT cells, enhance their cooperation with B cells, and which hold promise for vaccine development.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Barral P, Eckl-Dorna J, Harwood NE, et al. B cell receptor-mediated uptake of CD1d-restricted antigen augments antibody responses by recruiting invariant NKT cell help in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:8345–8350. In combination with Leadbetter et al. PNAS 2008, this study was among the first to demonstrate iNKT cell cognate help for B cells in vivo. The authors showed that particulate delivery of αGalCer together with a B cell antigen enhances antigen-specific B cell proliferation, extrafollicular PB expansion, and IgM and class-switched antibody responses. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Leadbetter EA, Brigl M, Illarionov P, et al. NK T cells provide lipid antigen-specific cognate help for B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:8339–8344. In combination with Barral et al. PNAS 2008, this study was the first to demonstrate cognate iNKT cell help for B cells in vivo. They authors used a haptenated glycolipid to demonstrate iNKT cells provide direct help to glycolipid-presenting CD1d+ B cells for antigen-specific proliferation and class switched antibody production. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

