Kibdelomycin is a potent and selective agent against toxigenic Clostridium difficile
- PMID: 24514098
- PMCID: PMC4023737
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00021-14
Kibdelomycin is a potent and selective agent against toxigenic Clostridium difficile
Abstract
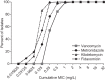
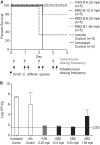
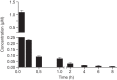
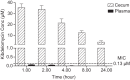
Clostridium difficile is the causative agent of C. difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD), with increased risk in elderly populations. Kibdelomycin, a novel natural-product inhibitor of type II topoisomerase enzymes, was evaluated for activity against C. difficile and gastrointestinal anaerobic organisms. Toxigenic C. difficile isolates (n=168) from U.S. hospitals and anaerobic Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms (n=598) from Chicago-area hospitals were tested. Kibdelomycin showed potent activity against toxigenic C. difficile (MIC90=0.25 μg/ml) and most Gram-positive aerobic organisms but had little activity against Bacteroides species (MIC50>32 μg/ml; n=270). Potent anti-C. difficile activity was also observed in the hamster model of C. difficile colitis. Dosing at 1.6 mg/kg (twice-daily oral dose) resulted in protection from a lethal infection and a 2-log reduction in C. difficile cecal counts. A 6.25-mg/kg twice-daily oral dose completely eliminated detectable C. difficile counts in cecal contents. A single 6.25-mg/kg oral dose showed that cecal contents were exposed to the drug at >2 μM (eightfold higher than the MIC), with no significant plasma exposure. These findings support further exploration of kibdelomycin for development of an anti-C. difficile agent.
Figures
References
-
- Miller BA, Chen LF, Sexton DJ, Anderson DJ. 2011. Comparison of the burdens of hospital-onset, healthcare facility-associated Clostridium difficile infection and of healthcare-associated infection due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in community hospitals. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 32:387–390. 10.1086/659156 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Petrella LA, Sambol SP, Cheknis A, Nagaro K, Kean Y, Sears PS, Babakhani F, Johnson S, Gerding DN. 2012. Decreased cure and increased recurrence rates for Clostridium difficile infection caused by the epidemic C. difficile BI strain. Clin. Infect. Dis. 55:351–357. 10.1093/cid/cis430 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Qin J, Li R, Raes J, Arumugam M, Burgdorf KS, Manichanh C, Nielsen T, Pons N, Levenez F, Yamada T, Mende DR, Li J, Xu J, Li S, Li D, Cao J, Wang B, Liang H, Zheng H, Xie Y, Tap J, Lepage P, Bertalan M, Batto JM, Hansen T, Le Paslier D, Linneberg A, Nielsen HB, Pelletier E, Renault P, Sicheritz-Ponten T, Turner K, Zhu H, Yu C, Li S, Jian M, Zhou Y, Li Y, Zhang X, Li S, Qin N, Yang H, Wang J, Brunak S, Dore J, Guarner F, Kristiansen K, Pedersen O, Parkhill J, Weissenbach J, Meta HITC, Bork P, Ehrlich SD, Wang J. 2010. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 464:59–65. 10.1038/nature08821 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

