Thioredoxin-interacting protein is a biomechanical regulator of Src activity: key role in endothelial cell stress fiber formation
- PMID: 24515523
- PMCID: PMC3981969
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.301315
Thioredoxin-interacting protein is a biomechanical regulator of Src activity: key role in endothelial cell stress fiber formation
Abstract
Rationale: Fluid shear stress differentially regulates endothelial cell stress fiber formation with decreased stress fibers in areas of disturbed flow compared with steady flow areas. Importantly, stress fibers are critical for several endothelial cell functions including cell shape, mechano-signal transduction, and endothelial cell-cell junction integrity. A key mediator of steady flow-induced stress fiber formation is Src that regulates downstream signaling mediators such as phosphorylation of cortactin, activity of focal adhesion kinase, and small GTPases.
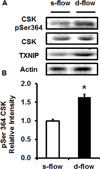
Objective: Previously, we showed that thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP, also VDUP1 [vitamin D upregulated protein 1] and TBP-2 [thioredoxin binding protein 2]) was regulated by fluid shear stress; TXNIP expression was increased in disturbed flow compared with steady flow areas. Although TXNIP was originally characterized for its role in redox and metabolic cellular functions, recent reports show important scaffold functions related to its α-arrestin structure. Based on these findings, we hypothesized that TXNIP acts as a biomechanical sensor that regulates Src kinase activity and stress fiber formation.
Methods and results: Using en face immunohistochemistry of the aorta and cultured endothelial cells, we show inverse relationship between TXNIP expression and Src activity. Specifically, steady flow increased Src activity and stress fiber formation, whereas it decreased TXNIP expression. In contrast, disturbed flow had opposite effects. We studied the role of TXNIP in regulating Src homology phosphatase-2 plasma membrane localization and vascular endothelial cadherin binding because Src homology phosphatase-2 indirectly regulates dephosphorylation of Src tyrosine 527 that inhibits Src activity. Using immunohistochemistry and immunoprecipitation, we found that TXNIP prevented Src homology phosphatase-2-vascular endothelial cadherin interaction.
Conclusions: In summary, these data characterize a fluid shear stress-mediated mechanism for stress fiber formation that involves a TXNIP-dependent vascular endothelial cadherin-Src homology phosphatase-2-Src pathway.
Keywords: TXNIP; disturbed flow; endothelial cells; laminar flow; stress fibers.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Thioredoxin interacting protein promotes endothelial cell inflammation in response to disturbed flow by increasing leukocyte adhesion and repressing Kruppel-like factor 2.Circ Res. 2012 Feb 17;110(4):560-8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.256362. Epub 2012 Jan 19. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 22267843 Free PMC article.
-
Thioredoxin-interacting protein mediates TRX1 translocation to the plasma membrane in response to tumor necrosis factor-α: a key mechanism for vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 transactivation by reactive oxygen species.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011 Aug;31(8):1890-7. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.226340. Epub 2011 Jun 2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011. PMID: 21636804
-
Fluid shear stress inhibits vascular inflammation by decreasing thioredoxin-interacting protein in endothelial cells.J Clin Invest. 2005 Mar;115(3):733-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI23001. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 15696199 Free PMC article.
-
Thioredoxin interacting protein: redox dependent and independent regulatory mechanisms.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012 Mar 15;16(6):587-96. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.4137. Epub 2011 Dec 20. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012. PMID: 21929372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein in Cancer and Diabetes.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022 May;36(13-15):1001-1022. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0038. Epub 2021 Oct 7. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022. PMID: 34384271 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Low or oscillatory shear stress and endothelial permeability in atherosclerosis.Front Physiol. 2024 Sep 9;15:1432719. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1432719. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39314624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sodium butyrate-activated TRAF6-TXNIP pathway affects A549 cells proliferation and migration.Cancer Med. 2020 May;9(10):3477-3488. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2564. Epub 2019 Oct 2. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 31578830 Free PMC article.
-
A pan-cancer analysis of thioredoxin-interacting protein as an immunological and prognostic biomarker.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Jul 17;22(1):230. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02639-2. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 35843949 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Expression of TXNIP in the peripheral leukocytes of patients with coronary atherosclerotic heart disease.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Dec;96(49):e9108. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009108. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 29245343 Free PMC article.
-
Does cardiac resynchronization therapy restore peripheral circulatory homeostasis?ESC Heart Fail. 2018 Feb;5(1):129-138. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12211. Epub 2017 Oct 13. ESC Heart Fail. 2018. PMID: 29030923 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakashima Y, Plump AS, Raines EW, Breslow JL, Ross R. ApoE-deficient mice develop lesions of all phases of atherosclerosis throughout the arterial tree. Arterioscler Thromb. 1994;14:133–140. - PubMed
-
- Caro CG, Fitz-Gerald JM, Schroter RC. Arterial wall shear and distribution of early atheroma in man. Nature. 1969;223:1159–1160. - PubMed
-
- VanderLaan PA, Reardon CA, Getz GS. Site Specificity of Atherosclerosis. Site-Selective Responses to Atherosclerotic Modulators. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003 Nov 6; - PubMed
-
- Malek AM, Alper SL, Izumo S. Hemodynamic shear stress and its role in atherosclerosis. Jama. 1999;282:2035–2042. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

