Molecular profiling of Mycobacterium tuberculosis identifies tuberculosinyl nucleoside products of the virulence-associated enzyme Rv3378c
- PMID: 24516143
- PMCID: PMC3939896
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1315883111
Molecular profiling of Mycobacterium tuberculosis identifies tuberculosinyl nucleoside products of the virulence-associated enzyme Rv3378c
Abstract
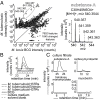
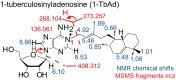
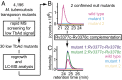
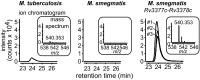
To identify lipids with roles in tuberculosis disease, we systematically compared the lipid content of virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis with the attenuated vaccine strain Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin. Comparative lipidomics analysis identified more than 1,000 molecular differences, including a previously unknown, Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific lipid that is composed of a diterpene unit linked to adenosine. We established the complete structure of the natural product as 1-tuberculosinyladenosine (1-TbAd) using mass spectrometry and NMR spectroscopy. A screen for 1-TbAd mutants, complementation studies, and gene transfer identified Rv3378c as necessary for 1-TbAd biosynthesis. Whereas Rv3378c was previously thought to function as a phosphatase, these studies establish its role as a tuberculosinyl transferase and suggest a revised biosynthetic pathway for the sequential action of Rv3377c-Rv3378c. In agreement with this model, recombinant Rv3378c protein produced 1-TbAd, and its crystal structure revealed a cis-prenyl transferase fold with hydrophobic residues for isoprenoid binding and a second binding pocket suitable for the nucleoside substrate. The dual-substrate pocket distinguishes Rv3378c from classical cis-prenyl transferases, providing a unique model for the prenylation of diverse metabolites. Terpene nucleosides are rare in nature, and 1-TbAd is known only in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Thus, this intersection of nucleoside and terpene pathways likely arose late in the evolution of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex; 1-TbAd serves as an abundant chemical marker of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and the extracellular export of this amphipathic molecule likely accounts for the known virulence-promoting effects of the Rv3378c enzyme.
Keywords: TbAd; terpenyl transferase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dye C, Glaziou P, Floyd K, Raviglione M. Prospects for tuberculosis elimination. Annu Rev Public Health. 2013;34:271–286. - PubMed
-
- Sturgill-Koszycki S, et al. Lack of acidification in Mycobacterium phagosomes produced by exclusion of the vesicular proton-ATPase. Science. 1994;263(5147):678–681. - PubMed
-
- Camus JC, Pryor MJ, Médigue C, Cole ST. Re-annotation of the genome sequence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. Microbiology. 2002;148(Pt 10):2967–2973. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

