Stromal cell-derived factor-1 and its receptor CXCR4 are upregulated expression in degenerated intervertebral discs
- PMID: 24516346
- PMCID: PMC3917111
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.7489
Stromal cell-derived factor-1 and its receptor CXCR4 are upregulated expression in degenerated intervertebral discs
Abstract
Background: Although chemokine stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1) and its receptor CXCR4 induce degradation of articular cartilage in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA), the association between the SDF-1/CXCR4 pathway and degradation of the cartilaginous endplate and nucleus pulposus has not been thoroughly clarified. We investigated the expression of SDF-1 and CXCR4 in intervertebral discs (IVDs).
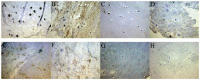
Methods: SDF-1 and CXCR4 levels in human IVDs and the rat L5/6 motion segment were quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. SDF-1 staining was quantified using a microscope and Image-Pro Plus software. Integrated optical density (IOD) served as the measurement parameter. The number of CXCR4 immunoreactive cells was expressed as a percentage of the total number of cells.
Results: SDF-1 and CXCR4 were both expressed in IVDs, and the levels of SDF-1 and CXCR4 were both significantly higher in the degeneration group than in the normal group of human (or rat) discs. Both nucleus pulposus cells and cartilaginous endplate cells expressed the CXCR4 protein. Furthermore, a positive correlation was observed between the SDF-1 IOD value and the percentage of CXCR4-positive disc cells in the nucleus pulposus and cartilaginous endplate. The SDF-1 IOD values were significantly higher in the outer annular fibrosus and bone/endplate junction region than in the nucleus pulposus and cartilaginous endplate in the rat specimens.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest upregulated expression of SDF-1 and its receptor CXCR4 in degenerated IVD.
Keywords: CXCR4; SDF-1; endplate; intervertebral disc; nucleus pulposus.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Freemont AJ, Watkins A, Le Maitre C. et al. Current understanding of cellular and molecular events in intervertebral disc degeneration: implications for therapy. J Pathol. 2002;196:374–379. - PubMed
-
- Cui Y, Yu J, Urban JP. et al. Differential gene expression profiling of metalloproteinases and their inhibitors: a comparison between bovine intervertebral disc nucleus pulposus cells and articular chondrocytes. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010;35(11):1101–1108. - PubMed
-
- Kim KW, Lim TH, Kim JG. et al. The origin of chondrocytes in the nucleus pulposus and histologic findings associated with the transition of a notochordal nucleus pulposus to a fibrocartilaginous nucleus pulposus in intact rabbit intervertebral discs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2003;28(10):982–990. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

