DNA double strand breaks as predictor of efficacy of the alpha-particle emitter Ac-225 and the electron emitter Lu-177 for somatostatin receptor targeted radiotherapy
- PMID: 24516620
- PMCID: PMC3917860
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088239
DNA double strand breaks as predictor of efficacy of the alpha-particle emitter Ac-225 and the electron emitter Lu-177 for somatostatin receptor targeted radiotherapy
Abstract
Rationale: Key biologic effects of the alpha-particle emitter Actinium-225 in comparison to the beta-particle emitter Lutetium-177 labeled somatostatin-analogue DOTATOC in vitro and in vivo were studied to evaluate the significance of γH2AX-foci formation.
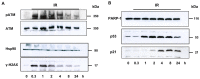
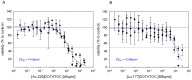
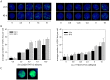
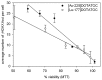
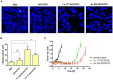
Methods: To determine the relative biological effectiveness (RBE) between the two isotopes (as - biological consequence of different ionisation-densities along a particle-track), somatostatin expressing AR42J cells were incubated with Ac-225-DOTATOC and Lu-177-DOTATOC up to 48 h and viability was analyzed using the MTT assay. DNA double strand breaks (DSB) were quantified by immunofluorescence staining of γH2AX-foci. Cell cycle was analyzed by flow cytometry. In vivo uptake of both radiolabeled somatostatin-analogues into subcutaneously growing AR42J tumors and the number of cells displaying γH2AX-foci were measured. Therapeutic efficacy was assayed by monitoring tumor growth after treatment with activities estimated from in vitro cytotoxicity.
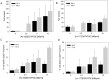
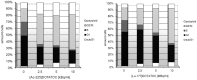
Results: Ac-225-DOTATOC resulted in ED50 values of 14 kBq/ml after 48 h, whereas Lu-177-DOTATOC displayed ED50 values of 10 MBq/ml. The number of DSB grew with increasing concentration of Ac-225-DOTATOC and similarly with Lu-177-DOTATOC when applying a factor of 700-fold higher activity compared to Ac-225. Already 24 h after incubation with 2.5-10 kBq/ml, Ac-225-DOTATOC cell-cycle studies showed up to a 60% increase in the percentage of tumor cells in G2/M phase. After 72 h an apoptotic subG1 peak was also detectable. Tumor uptake for both radio peptides at 48 h was identical (7.5%ID/g), though the overall number of cells with γH2AX-foci was higher in tumors treated with 48 kBq Ac-225-DOTATOC compared to tumors treated with 30 MBq Lu-177-DOTATOC (35% vs. 21%). Tumors with a volume of 0.34 ml reached delayed exponential tumor growth after 25 days (44 kBq Ac-225-DOTATOC) and after 21 days (34 MBq Lu-177-DOTATOC).
Conclusion: γH2AX-foci formation, triggered by beta- and alpha-irradiation, is an early key parameter in predicting response to internal radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Reubi JC (2003) Peptide receptors as molecular targets for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Endocr Rev 24: 389–427. - PubMed
-
- McDevitt MR, Sgouros G, Finn RD, Humm JL, Jurcic JG, et al. (1998) Radioimmunotherapy with alpha-emitting nuclides. Eur J Nucl Med 25: 1341–1351. - PubMed
-
- Dadachova E (2010) Cancer therapy with alpha-emitters labeled peptides. Semin Nucl Med 40: 204–208. - PubMed
-
- Morgenstern A, Bruchertseifer F, Apostolidis C (2011) Targeted alpha therapy with 213Bi. Curr Radiopharm 4: 295–305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

