Cross-link formation and peptidoglycan lattice assembly in the FemA mutant of Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 24517508
- PMCID: PMC3985804
- DOI: 10.1021/bi4016742
Cross-link formation and peptidoglycan lattice assembly in the FemA mutant of Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
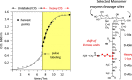
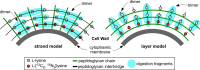
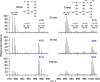
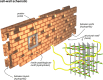
Staphylococcus aureus FemA mutant grown in the presence of an alanine-racemase inhibitor was labeled with d-[1-(13)C]alanine, l-[3-(13)C]alanine, [2-(13)C]glycine, and l-[5-(19)F]lysine to characterize some details of the peptidoglycan tertiary structure. Rotational-echo double-resonance (REDOR) NMR of isolated cell walls was used to measure internuclear distances between (13)C-labeled alanines and (19)F-labeled lysine incorporated in the peptidoglycan. The alanyl (13)C labels were preselected for REDOR measurement by their proximity to the glycine label using (13)C-(13)C spin diffusion. The observed (13)C-(13)C and (13)C-(19)F distances are consistent with a tightly packed, hybrid architecture containing both parallel and perpendicular stems in a repeating structural motif within the peptidoglycan.
Figures
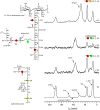
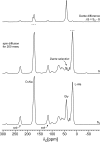

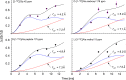
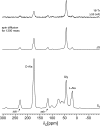


References
-
- Rogers H. J., Ward J. B., and Perkins H. R. (1980) Microbial Cell Walls and Membranes, Chapman and Hall, New York.
-
- Gullion T.; Schaefer J. (1989) Rotational-echo double-resonance NMR. J. Magn. Reson. 81, 196–200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

