Controlled release of an anti-cancer drug from DNA structured nano-films
- PMID: 24518218
- PMCID: PMC3921640
- DOI: 10.1038/srep04078
Controlled release of an anti-cancer drug from DNA structured nano-films
Abstract
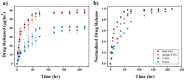
We demonstrate the generation of systemically releasable anti-cancer drugs from multilayer nanofilms. Nanofilms designed to drug release profiles in programmable fashion are promising new and alternative way for drug delivery. For the nanofilm structure, we synthesized various unique 3-dimensional anti cancer drug incorporated DNA origami structures (hairpin, Y, and X shaped) and assembled with peptide via layer-by-layer (LbL) deposition method. The key to the successful application of these nanofilms requires a novel approach of the influence of DNA architecture for the drug release from functional nano-sized surface. Herein, we have taken first steps in building and controlling the drug incorporated DNA origami based multilayered nanostructure. Our finding highlights the novel and unique drug release character of LbL systems in serum condition taken full advantages of DNA origami structure. This multilayer thin film dramatically affects not only the release profiles but also the structure stability in protein rich serum condition.
Figures


References
-
- Fu H. L., Cheng S. X., Zhang X. Z. & Zhuo R. X. Dendrimer/DNA complexes encapsulated functional biodegradable polymer for substrate-mediated gene delivery. J. Gene Med. 10, 1334–1342 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Eckardt L. H. et al. DNA nanotechnology: Chemical copying of connectivity. Nature 420, 286 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Sano T., Smith C. L. & Cantor C. R. Immuno-Pcr - Very Sensitive Antigen-Detection by Means of Specific Antibody-DNA Conjugates. Science 258, 120–122 (1992). - PubMed
-
- Zhang J. T., Chua L. S. & Lynn D. M. Multilayered thin films that sustain the release of functional DNA under physiological conditions. Langmuir 20, 8015–8021 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Elghanian R. et al. Selective colorimetric detection of polynucleotides based on the distance-dependent optical properties of gold nanoparticles. Science 277, 1078–1081 (1997). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

