Can Doppler or contrast-enhanced ultrasound analysis add diagnostically important information about the nature of breast lesions?
- PMID: 24519198
- PMCID: PMC3912319
- DOI: 10.6061/clinics/2014(02)03
Can Doppler or contrast-enhanced ultrasound analysis add diagnostically important information about the nature of breast lesions?
Abstract
Objectives: Despite evidence suggesting that Doppler ultrasonography can help to differentiate between benign and malignant breast lesions, it is rarely applied in clinical practice. The aim of this study was to determine whether certain vascular features of breast masses observed by duplex Doppler and color Doppler ultrasonography (before and/or after microbubble contrast injection) add information to the gray-scale analysis and support the Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) classification.
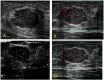
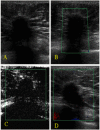
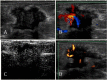
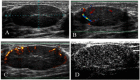
Methods: Seventy solid lesions were prospectively evaluated with gray-scale ultrasonography, color Doppler ultrasonography, and contrast-enhanced ultrasonography. The morphological analysis and lesion vascularity were correlated with the histological results.
Results: Percutaneous core biopsies revealed that 25/70 (17.5%) lesions were malignant, while 45 were benign. Hypervascular lesions with tortuous and central vessels, a resistive index (RI)≥ 0.73 before contrast injection, and an RI≥ 0.75 after contrast injection were significantly predictive of malignancy (p<0.001).
Conclusion: The combination of gray-scale ultrasonography data with unenhanced or enhanced duplex Doppler and color Doppler US data can provide diagnostically useful information. These techniques can be easily implemented because Doppler devices are already present in most health centers.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Contrast-enhanced power Doppler sonography in breast lesions: effect on differential diagnosis after mammography and gray scale sonography.J Ultrasound Med. 2004 Feb;23(2):183-95; quiz 196-7. doi: 10.7863/jum.2004.23.2.183. J Ultrasound Med. 2004. PMID: 14992355
-
The use of breast ultrasound color Doppler vascular pattern morphology improves diagnostic sensitivity with minimal change in specificity.Ultraschall Med. 2010 Oct;31(5):466-74. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1109478. Epub 2010 Jan 21. Ultraschall Med. 2010. PMID: 20094978
-
Power Doppler sonography: evaluation of solid breast lesions and correlation with lymph node metastasis.Clin Imaging. 2008 May-Jun;32(3):167-71. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2007.12.004. Clin Imaging. 2008. PMID: 18502342
-
Value of contrast-enhanced power Doppler sonography using a microbubble echo-enhancing agent in evaluation of small breast lesions.J Clin Ultrasound. 2003 Jun;31(5):227-38. doi: 10.1002/jcu.10172. J Clin Ultrasound. 2003. PMID: 12767017 Clinical Trial.
-
Ultrasound-Based Noncontrast Microvascular Imaging for Evaluation of Breast Lesions: Imaging Techniques and Review of Diagnostic Criteria.Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2024 Mar 17;34(4):702-713. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1782162. eCollection 2024 Oct. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39318571 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis comparing the diagnostic capability of automated breast ultrasound and contrast-enhanced ultrasound in breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 9;13:1305545. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1305545. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38264749 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging Considerations and Interprofessional Opportunities in the Care of Breast Cancer Patients in the Neoadjuvant Setting.Semin Oncol Nurs. 2017 Nov;33(4):425-439. doi: 10.1016/j.soncn.2017.08.008. Epub 2017 Sep 15. Semin Oncol Nurs. 2017. PMID: 28927763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Superb Microvascular Imaging Technology Can Improve the Diagnostic Efficiency of the BI-RADS System.Front Oncol. 2021 Jun 24;11:634752. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.634752. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34249681 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic utility of ultrasonography in the management of postoperative fluid collections and abdominal indwelling catheters following pancreaticoduodenectomy: retrospective cohort study.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Apr 23;30(1):319. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02590-8. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40270062 Free PMC article.
-
Microvascular Ultrasonic Imaging of Angiogenesis Identifies Tumors in a Murine Spontaneous Breast Cancer Model.Int J Biomed Imaging. 2020 Feb 6;2020:7862089. doi: 10.1155/2020/7862089. eCollection 2020. Int J Biomed Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32089667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leconte I, Feger C, Galant C, Berlière G, Berg BV, D'Hoore W, et al. Mammography and subsequent whole-breast sonography of nonpalpable breast cancers: the importance of radiologic breast density. Am J Roentgenol. 2003;180(6):1675–9. - PubMed
-
- Chala L, Endo E, Kim S, de Castro F, Moraes P, Cerri G, et al. Gray-scale sonography of solid breast masses diagnosis of probably benign masses and reduction of the number of biopsies. J Clin Ultrasound. 2007;35(1):9–19. - PubMed
-
- American College of Radiology. 4th ed American College of Radiology. (ACR): 2003. Ilustrated Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System Atlas (BI-RADS®): Ultrasound.
-
- Less JR, Skalak TC, Sevick EM, Jain RK. Microvascular architecture in a mammary carcinoma: branching patterns and vessel dimensions. Cancer Res. 1991;51(1):265–73. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

