Psychological and behavioural treatments for adults with non-epileptic attack disorder
- PMID: 24519702
- PMCID: PMC11032749
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006370.pub2
Psychological and behavioural treatments for adults with non-epileptic attack disorder
Abstract
Background: Psychogenic non-epileptic seizures, also known as non-epileptic attack disorder (NEAD), have the outward appearance of epilepsy in the absence of physiological or electroencephalographic correlates. Non-epileptic seizures can occur in isolation or in combination with epileptic seizures. The development and maintenance of non-epileptic seizures has been well documented and there is a growing literature on the treatment of non-epileptic seizures which includes non-psychological (including anti-anxiety and antidepressant pharmacological treatment) and psychological therapies (including cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT), hypnotherapy and paradoxical therapy). Various treatment methodologies have been tried with variable success. The purpose of this Cochrane review was to establish the evidence base for the treatment of non-epileptic seizures with behavioural and psychological therapies only.
Objectives: To assess whether behavioural or psychological treatments for non-epileptic seizures or NEAD result in a reduction in the frequency of seizures or improvement in quality of life, or both, and whether any treatment is significantly more effective than others.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Epilepsy Group's Specialised Register (4 February 2013), the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library 2013, Issue 1) (January 2013), MEDLINE (1946 to 4 February 2013), PsycINFO (4 February 2013) and SCOPUS (4 February 2013). No language restrictions were imposed. We checked the reference lists of retrieved studies for additional reports of relevant studies
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and before and after controlled and non-controlled studies were eligible for inclusion. Studies were required to assess one or more types of behavioural or psychological interventions, or both, for the treatment of non-epileptic seizures. Studies of childhood non-epileptic seizures were excluded from our review.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors (JM, JP) independently assessed the trials for inclusion and extracted data. Outcomes included reduction in seizure frequency and improvements in quality of life.
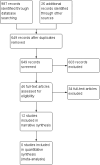
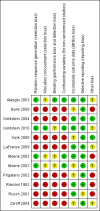
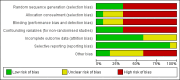
Main results: Twelve studies, with a total of 343 participants, met our inclusion criteria (four RCTs and eight before and after non-controlled studies). Of the four RCTs, one examined patients with non-epileptic seizures and three had a mixed diagnosis (pseudoseizures, conversion disorder and somatisation disorder). Most of the non-randomised studies used non-epileptic seizure patients exclusively. Overall, five studies examined the effectiveness of psychotherapy, three examined CBT, two investigated hypnosis, one assessed paradoxical intention and one had a mixed intervention design. We classified two included studies as low risk of bias, one as unclear and nine as high risk of bias. Meta-analysis could not be undertaken due to the heterogeneity of design and interventions. Most included studies reported improved outcomes for the intervention under investigation. One RCT investigating the effectiveness of CBT in this patient group found a significant reduction in seizure frequency compared to controls (P < 0.001).
Authors' conclusions: There is little reliable evidence to support the use of any treatment, including CBT, in the treatment of non-epileptic seizures. Further randomised controlled trials of CBT and other interventions are needed.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures
Update of
-
Treatments for non-epileptic attack disorder.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD006370. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006370. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Feb 11;(2):CD006370. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006370.pub2. PMID: 17253591 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Ataoglu 2003 {published data only}
Barry 2008 {published data only}
-
- Barry J, Wittenberg D, Bullock K, Michaels J, Classen C, Fisher R. Group therapy for patients with psychogenic nonepileptic seizures: a pilot study. Epilepsy and Behavior 2008;13(4):624‐9. - PubMed
Goldstein 2004 {published data only}
-
- Goldstein LH, Deale AC, Mitchell‐O'Malley SJ, Toone BK, Mellers JDC. An evaluation of cognitive behavioral therapy as a treatment for dissociative seizures: a pilot study. Cognitive and Behavioral Neurology 2004;17(1):41‐9. - PubMed
Goldstein 2010 {published data only}
Kuyk 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kuyk J, Siffels MC, Bakvis P, Swinkels WAM. Psychological treatment of patients with psychogenic non‐epileptic seizures: an outcome study. Seizure 2008;17(7):595‐603. - PubMed
LaFrance 2009 {published data only}
-
- LaFrance WC Jr, Miller IW, Ryan CE, Blum AS, Solomon DA, Kelley JE, et al. Cognitive behavioural therapy for psychogenic nonepileptic seizures. Epilepsy and Behavior 2009;14(4):591‐6. - PubMed
Moene 2002 {published data only}
-
- Moene FC, Spinhoven P, Hoogduin KA, Dyck R. A randomised controlled clinical trial on the additional effect of hypnosis in a comprehensive treatment programme for in‐patients with conversion disorder of the motor type. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics 2002;71(2):66‐76. - PubMed
Moene 2003 {published data only}
-
- Moene FC, Spinhoven P, Hoogduin KA, Dyck R. A randomized controlled clinical trial of a hypnosis‐based treatment for patients with conversion disorder, motor type. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hypnosis 2003;51(1):29‐50. - PubMed
Prigatano 2002 {published data only}
-
- Prigatano GP, Stonnington CM, Fisher RS. Psychological factors in the genesis and management of nonepileptic seizures: clinical observations. Epilepsy and Behavior 2002;3(4):343‐9. - PubMed
Ramani 1982 {published data only}
-
- Ramani V, Gumnit RJ. Management of hysterical seizures in epileptic patients. Archives of Neurology 1982;39(2):78‐81. - PubMed
Rusch 2001 {published data only}
-
- Rusch MD, Morris GL, Allen L, Lathrop L. Psychological treatment of nonepileptic events. Epilepsy and Behavior 2001;2(3 Pt 1):277‐83. - PubMed
Zaroff 2004 {published data only}
-
- Zaroff CM, Myers L, Barr WB, Luciano D, Devinsky O. Group psychoeducation as treatment for psychological nonepileptic seizures. Epilepsy and Behavior 2004;5(4):587‐92. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Allen 2006 {published data only}
-
- Allen LA, Woolfolk RL, Escobar JI, Gara MA, Hamer RM. Cognitive‐behavioral therapy for somatization disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Internal Medicine 2006;166(14):1512‐8. - PubMed
Betts 1992 {published data only}
-
- Betts T, Boden S. Diagnosis, management and prognosis of a group of 128 patients with non‐epileptic attack disorder. Part 1. Seizure: European Journal of Epilepsy 1992;1(1):19‐26. - PubMed
Bhatia 2005 {published data only}
-
- Bhatia MS, Sapra S. Pseudoseizures in children: a profile of 50 cases. Clinical Pediatrics 2005;44(7):617‐21. - PubMed
Bleichhardt 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bleichhardt G, Timmer B, Rief W. Cognitive‐behavioural therapy for patients with multiple somatoform symptoms‐a randomised controlled trial in tertiary care. Journal of Psychosomatic Research 2004;56(4):449‐54. - PubMed
Buchanan 1993 {published data only}
-
- Buchanan N, Snars J. Pseudoseizures (non epileptic attack disorder)‐clinical management and outcome in 50 patients. Seizure 1993;2(2):141‐6. - PubMed
Chinta 2008 {published data only}
Elsas 2011 {published data only}
-
- Elsas SM, Gregory WL, White G, Navarro G, Salinsky MC, Andrews DJ. Aura interruption: the Andrews/Reiter behavioral intervention may reduce seizures and improve quality of life: a pilot trial. Epilepsy and Behavior 2011;22(4):765‐72. - PubMed
Flom 1999 {published data only}
-
- Flom J. The effects of psychotherapy on psychogenic seizures. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses. Seattle University, 1999.
Ghosh 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ghosh JK, Majumder P, Pant P, Dutta R, Bhatia BD. Clinical profile and outcome of conversion disorder in children in a tertiary hospital of north India. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 2007;53(3):213‐4. - PubMed
Gupta 2011 {published data only}
-
- Gupta V, Singh A, Upadhyay S, Bhatia B. Clinical profile of somatoform disorders in children. Indian Journal of Pediatrics 2011;78(3):283‐6. - PubMed
Hiller 2003 {published data only}
-
- Hiller W, Fichter MM, Rief W. A controlled treatment study of somatoform disorders including analysis of healthcare utilization and cost‐effectiveness. Journal of Psychosomatic Research 2003;54(4):369‐80. - PubMed
Hovorka 2007 {published data only}
-
- Hovorka J, Nezadal T, Herman E, Nemcova I, Bajacek M. Psychogenic non‐epileptic seizures, prospective clinical experience: diagnosis, clinical features, risk factors, psychiatric comorbidity, treatment outcome. Epileptic Disorders 2007;9(Suppl 1):S52‐8. - PubMed
Kashner 1995 {published data only}
-
- Kashner TM, Rost K, Cohen B, Anderson M, Smith GR. Enhancing the health of somatization disorder patients. Effectiveness of short‐term group therapy. Psychosomatics 1995;36(5):462‐70. - PubMed
Katsamanis 2011 {published data only}
Khattak 2006 {published data only}
-
- Khattak T, Farooq S, Jan B. Behavior therapy in dissociative convulsions disorder. Journal of the College of Physicians and Surgeons Pakistan 2006;16(5):359‐63. - PubMed
Lidbeck 1997 {published data only}
-
- Lidbeck J. Group therapy for somatization disorders in general practice: effectiveness of a short cognitive‐behavioural treatment model. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1997;96(1):14‐24. - PubMed
Lidbeck 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lidbeck J. Group therapy for somatization disorders in primary care: maintenance of treatment goals of short cognitive‐behavioral treatment one‐and‐a‐half‐year follow‐up. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 2003;107(6):449‐56. - PubMed
Magallon 2008 {published data only}
Martin 2007 {published data only}
-
- Martin A, Rauh E, Fichter M, Rief W. A one‐session treatment for patients suffering from medically unexplained symptoms in primary care: a randomized clinical trial. Psychosomatics 2007;48(4):294‐303. - PubMed
Mayor 2010 {published data only}
-
- Mayor R, Howlett S, Grunewald R, Reuber M. Long‐term outcome of brief augmented psychodynamic interpersonal therapy for psychogenic nonepileptic seizures: seizure control and health care utilization. Epilepsia 2010;51(7):1169‐76. - PubMed
McDade 1992 {published data only}
-
- McDade G, Brown SW. Non‐epileptic seizures: management and predictive factors of outcome. Seizure 1992;1(1):7‐10. - PubMed
McLeod 1997 {published data only}
-
- McLeod CC, Budd MA, McClelland DC. Treatment of somatization in primary care. General Hospital Psychiatry 1997;19(4):251‐8. - PubMed
Miller 1983 {published data only}
-
- Miller HR. Psychogenic seizures treated by hypnosis. American Journal of Clinical Hypnosis 1983;25(4):248‐52. - PubMed
Mims 1994 {published data only}
-
- Mims J, Antonello JL. Treatment of nonepileptic psychogenic events in adolescent patients using the systems model for intervention. Journal of Neuroscience Nursing 1994;26(5):298‐305. - PubMed
Nanke 2000 {published data only}
-
- Nanke A, Rief W. Biofeedback in the treatment of somatoform disorders. Verhaltenstherapie 2000;10(4):238‐48.
Nanke 2003 {published data only}
-
- Nanke A, Rief W. Biofeedback‐based interventions in somatoform disorders: a randomized controlled trial. Acta Neuropsychiatrica 2003;15(4):249‐56. - PubMed
Posse 2004 {published data only}
-
- Posse M. Jungian psychotherapy for somatization. European Journal of Psychiatry 2004;18(1):23‐9.
Schweickhardt 2007 {published data only}
-
- Schweickhardt A, Larisch A, Wirsching M, Fritzsche K. Short‐term psychotherapeutic interventions for somatizing patients in the general hospital: a randomized controlled study. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics 2007;76(6):339‐46. - PubMed
Share 1996 {published data only}
-
- Share IA. Dynamic psychotherapy for psychogenic nonepileptic seizures. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 1996;71(11):1125. - PubMed
Smith 1986 {published data only}
-
- Smith G, Monson R, Ray C. Psychiatric consultation in somatization disorder: a randomized controlled study. New England Journal of Medicine 1986;314(22):1407‐13. - PubMed
Smith 2009 {published data only}
Speckens 1996 {published data only}
-
- Speckens AEM, Van HAM, Spinhoven P, Hawton KE, Bolk JH, Rooijmans HGM. Favourable effects of cognitive behavioural therapy on unexplained physical symptoms: a randomized trial. Nederlands Tijdschrift Voor Geneeskunde 1996;140(23):1227‐32.
Timmer 2004 {published data only}
-
- Timmer B, Bleichhardt G, Rief W. Effectiveness of a cognitive‐behavioral group therapy for somatization: results of a randomized controlled trial in tertiary care. Zeitschrift fur Klinische Psychologie und Psychotherapie 2004;33(1):24‐32.
Timmer 2006 {published data only}
-
- Timmer B, Bleichhardt G, Rief W. Importance of psychotherapy motivation in patients with somatization syndrome. Psychotherapy Research 2006;16(3):348‐56.
References to studies awaiting assessment
La France {unpublished data only}
-
- LaFrance W, Webb A, Blum A, Keitner G, Barry J, Szaflarski J. Multi‐center treatment trial pilot for psychogenic nonepileptic seizures. American Epilepsy Society. 2012.
Additional references
Ataoglu 1998
-
- Ataoglu A, Sir A, Ozkan, M. Paradoxical therapy in conversion disorder. Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences 1998;28:419‐21.
Betts 1993
-
- Betts T, Duffy N. Non‐epileptic attack disorder (pseudoseizures) and sexual abuse: a review. In: Gram L, Johannessen SI, Osterman PO, Sillanpää M editor(s). Pseudo Epileptic Seizures. Petersfield: Wrightson Biomedical, 1993:55‐65.
Bodde 2009
-
- Bodde N, Brooks J, Baker G, Boon P, Hendriksen J, Mulder O, et al. Psychogenic non‐epileptic seizures‐‐definition, etiology, treatment and prognostic issues: a critical review. Seizure 2009;18:543‐53. - PubMed
Chemali 2004
-
- Chemali Z, Meadows M. The use of eye movement desensitization and reprocessing in the treatment of psychogenic seizures. Epilepsy & Behavior 2004;5(5):784‐7. - PubMed
Devinsky 1998
-
- Devinsky O. Nonepileptic psychogenic seizures: quagmires of pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. Epilepsia 39;5:458‐62. - PubMed
Duncan 2011
-
- Duncan R, Razvi S, Mulhern S. Newly presenting psychogenic nonepileptic seizures: incidence, population, characteristics and early outcome from a prospective audit of a first seizure clinic. Epilepsy and Behavior 2011;20:308‐11. - PubMed
Francis 1999a
-
- Francis P, Baker GA. Non‐epileptic attack disorder (NEAD): a comprehensive review. Seizure 1999;8:53‐61. - PubMed
Francis 1999b
-
- Francis PL, Baker GA, Appleton PL. Stress and avoidance in pseudoseizures: testing the assumptions. Epilepsy Research 1999;34:241‐9. - PubMed
Kirkham 2010
-
- Kirkham J, Dwan K, Altman D, Gamble C, Dodd S, Smyth R, et al. The impact of outcome reporting bias in randomised controlled trials on a cohort of systematic reviews. BMJ 2010;340:365. - PubMed
Lesser 2003
Martin 2003
-
- Martin R, Bell B, Hermann B, Mennemeyer S. Non epileptic seizures and their costs: the role neuropsychology. In: Pritigano GP, Pliskin NH editor(s). Clinical Neuropsychology and Cost Outcome Research: a Beginning. NY, USA: Psychology Press, 2003:235‐58.
Moene 1998
-
- Moene FC, Hoogduin K AL, Dyck R. The inpatient treatment of patients suffering from (motor) conversion symptoms: a description of eight cases. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hypnosis 1998;46(2):171‐90. - PubMed
NEAD Trust
-
- NEAD Trust. Seizures and symptoms. http://www.neadtrust.co.uk/seizuressymptoms.html (accessed 2 November 2012).
Non‐Epileptic Attacks
-
- Non‐epileptic attacks. http://www.nonepilepticattacks.info/2_common.html (accessed 2 November 2012).
Ramani 1993
-
- Ramani V. Review of psychiatric treatment strategies in non‐epileptic seizures. In: Rowan AJ, Gates JR editor(s). Non‐Epileptic Seizures. MA, USA: Butterworth‐Heinemann, 1993:259‐67.
Reilly 1999
-
- Reilly J, Baker GA, Rhodes J, Salmon P. The association of sexual and physical abuse with somatization: characteristics of patients presenting with irritable bowel syndrome and non‐epileptic attack disorder. Psychological Medicine 1999;29:399‐406. - PubMed
Reuber 2005
-
- Reuber M, Howlett S, Kemp S. Psychologic treatment of patients with psychogenic nonepileptic seizures. Expert Review in Neurotherapeutics 2005;5(6):737‐52. - PubMed
Sharpe 2011
Stone 2004
-
- Stone J, Sharpe M, Binzer M. Motor conversion symptoms and pseudoseizures: a comparison of clinical characteristics. Psychosomatics 2004;45:492‐9. - PubMed
Szaflarski 2000
-
- Szaflarski J, Ficker D, Cahill W, Privitera M. Four‐year incidence of psychogenic nonepileptic seizures in adults in Hamilton County, OH. Neurology 2000;55:1561‐3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous