Cyclooxygenase-2 in endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells restrains atherogenesis in hyperlipidemic mice
- PMID: 24519928
- PMCID: PMC4006304
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.007913
Cyclooxygenase-2 in endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells restrains atherogenesis in hyperlipidemic mice
Abstract
Background: Placebo-controlled trials of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs selective for inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) reveal an emergent cardiovascular hazard in patients selected for low risk of heart disease. Postnatal global deletion of COX-2 accelerates atherogenesis in hyperlipidemic mice, a process delayed by selective enzyme deletion in macrophages.
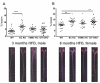
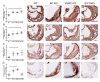
Methods and results: In the present study, selective depletion of COX-2 in vascular smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells depressed biosynthesis of prostaglandin I2 and prostaglandin E2, elevated blood pressure, and accelerated atherogenesis in Ldlr knockout mice. Deletion of COX-2 in vascular smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells coincided with an increase in COX-2 expression in lesional macrophages and increased biosynthesis of thromboxane. Increased accumulation of less organized intimal collagen, laminin, α-smooth muscle actin, and matrix-rich fibrosis was also apparent in lesions of the mutants.
Conclusions: Although atherogenesis is accelerated in global COX-2 knockouts, consistent with evidence of risk transformation during chronic nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug administration, this masks the contrasting effects of enzyme depletion in macrophages versus vascular smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells. Targeting delivery of COX-2 inhibitors to macrophages may conserve their efficacy while limiting cardiovascular risk.
Keywords: atherogenesis; cyclooxygenase; endothelial cell; prostaglandin; vascular smooth muscle.
Figures

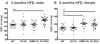


References
-
- FitzGerald GA. Cox-2 in play at the aha and the fda. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2007;28:303–307. - PubMed
-
- Bertagnolli MM, Eagle CJ, Zauber AG, Redston M, Solomon SD, Kim K, Tang J, Rosenstein RB, Wittes J, Corle D, Hess TM, Woloj GM, Boisserie F, Anderson WF, Viner JL, Bagheri D, Burn J, Chung DC, Dewar T, Foley TR, Hoffman N, Macrae F, Pruitt RE, Saltzman JR, Salzberg B, Sylwestrowicz T, Gordon GB, Hawk ET, Investigators APCS Celecoxib for the prevention of sporadic colorectal adenomas. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:873–884. - PubMed
-
- Bresalier RS, Sandler RS, Quan H, Bolognese JA, Oxenius B, Horgan K, Lines C, Riddell R, Morton D, Lanas A, Konstam MA, Baron JA, Adenomatous Polyp Prevention on Vioxx Trial I Cardiovascular events associated with rofecoxib in a colorectal adenoma chemoprevention trial. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1092–1102. - PubMed
-
- Solomon SD, McMurray JJ, Pfeffer MA, Wittes J, Fowler R, Finn P, Anderson WF, Zauber A, Hawk E, Bertagnolli M, Adenoma Prevention with Celecoxib Study I Cardiovascular risk associated with celecoxib in a clinical trial for colorectal adenoma prevention. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1071–1080. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

