The microRNA expression signature of bladder cancer by deep sequencing: the functional significance of the miR-195/497 cluster
- PMID: 24520312
- PMCID: PMC3919700
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084311
The microRNA expression signature of bladder cancer by deep sequencing: the functional significance of the miR-195/497 cluster
Abstract
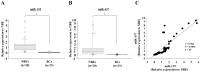
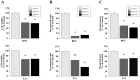
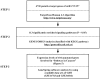
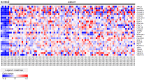
Current genome-wide microRNA (miRNA) expression signature analysis using deep sequencing technologies can drive the discovery of novel cancer pathways regulated by oncogenic and/or tumor suppressive miRNAs. We determined the genome-wide miRNA expression signature in bladder cancer (BC) by deep sequencing technology. A total of ten small RNA libraries were sequenced (five BCs and five samples of histologically normal bladder epithelia (NBE)), and 13,190,619 to 18,559,060 clean small RNA reads were obtained. A total of 933 known miRNAs and 17 new miRNA candidates were detected in this analysis. Among the known miRNAs, a total of 60 miRNAs were significantly downregulated in BC compared with NBE. We also found that several miRNAs, such as miR-1/133a, miR-206/133b, let-7c/miR-99a, miR-143/145 and miR-195/497, were located close together at five distinct loci and constituted clustered miRNAs. Among these clustered miRNAs, we focused on the miR-195/497 cluster because this clustered miRNA had not been analyzed in BC. Transfection of mature miR-195 or miR-497 in two BC cell lines (BOY and T24) significantly inhibited cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion, suggesting that the miR-195/497 cluster functioned as tumor suppressors in BC. Regarding the genes targeted by the miR-195/497 cluster, the TargetScan algorithm showed that 6,730 genes were putative miR-195/497 targets, and 113 significantly enriched signaling pathways were identified in this analysis. The "Pathways in cancer" category was the most enriched, involving 104 candidate target genes. Gene expression data revealed that 27 of 104 candidate target genes were actually upregulated in BC clinical specimens. Luciferase reporter assays and Western blotting demonstrated that BIRC5 and WNT7A were directly targeted by miR-195/497. In conclusion, aberrant expression of clustered miRNAs was identified by deep sequencing, and downregulation of miR-195/497 contributed to BC progression and metastasis. Tumor suppressive miRNA-mediated cancer pathways provide new insights into the potential mechanisms of BC oncogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dual regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase genes EGFR and c-Met by the tumor-suppressive microRNA-23b/27b cluster in bladder cancer.Int J Oncol. 2015 Feb;46(2):487-96. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2752. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Int J Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25405368 Free PMC article.
-
Dual tumor-suppressors miR-139-5p and miR-139-3p targeting matrix metalloprotease 11 in bladder cancer.Cancer Sci. 2016 Sep;107(9):1233-42. doi: 10.1111/cas.13002. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Cancer Sci. 2016. PMID: 27355528 Free PMC article.
-
Novel molecular targets regulated by tumor suppressors microRNA-1 and microRNA-133a in bladder cancer.Int J Oncol. 2012 Jun;40(6):1821-30. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1391. Epub 2012 Feb 29. Int J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22378464
-
Aberrant expression of microRNAs in bladder cancer.Nat Rev Urol. 2013 Jul;10(7):396-404. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2013.113. Epub 2013 May 28. Nat Rev Urol. 2013. PMID: 23712207 Review.
-
miRNAs role in bladder cancer pathogenesis and targeted therapy: Signaling pathways interplay - A review.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Feb;242:154316. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154316. Epub 2023 Jan 20. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 36682282 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic expression analysis of peripheral blood derived small extracellular vesicle miRNAs in sepsis progression.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jan;28(2):e18053. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18053. Epub 2023 Nov 28. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38014923 Free PMC article.
-
Treasures from trash in cancer research.Oncotarget. 2022 Nov 17;13:1246-1257. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28308. Oncotarget. 2022. PMID: 36395362 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased expression of let-7c is associated with non-response of muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients to neoadjuvant chemotherapy.Genes Cancer. 2016 Mar;7(3-4):86-97. doi: 10.18632/genesandcancer.103. Genes Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27382433 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated genes targeted by microRNAs and metabolic pathways in bladder cancer revealed by bioinformatics methods.Oncol Lett. 2018 Jun;15(6):9617-9624. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8602. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29928337 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA CASC9 positively regulates CHK1 to promote breast cancer cell proliferation and survival through sponging the miR‑195/497 cluster.Int J Oncol. 2019 May;54(5):1665-1675. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2019.4734. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Int J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30816435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2012) Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 62: 10–29. - PubMed
-
- Center for Cancer Control and Information Services, National Cancer Center, Japan. Available: http://ganjoho.jp/professional/statistics/statistics.html#01.
-
- Zuiverloon TC, Nieuweboer AJ, Vékony H, Kirkels WJ, Bangma CH, et al. (2012) Markers predicting response to bacillus Calmette-Guérin immunotherapy in high-risk bladder cancer patients: a systematic review. Eur Urol 61: 128–145. - PubMed
-
- Luke C, Tracey E, Stapleton A, Roder D (2010) Exploring contrary trends in bladder cancer incidence, mortality and survival: implications for research and cancer control. Intern Med J 40: 357–362. - PubMed
-
- Meeks JJ, Bellmunt J, Bochner BH, Clarke NW, Daneshmand S, et al. (2012) A systematic review of neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur Urol 62: 523–533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

