Spatial reorganization of putaminal dopamine D2-like receptors in cranial and hand dystonia
- PMID: 24520350
- PMCID: PMC3919754
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088121
Spatial reorganization of putaminal dopamine D2-like receptors in cranial and hand dystonia
Abstract
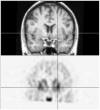
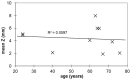
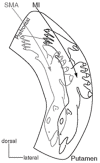
The putamen has a somatotopic organization of neurons identified by correspondence of firing rates with selected body part movements, as well as by complex, but organized, differential cortical projections onto putamen. In isolated focal dystonia, whole putaminal binding of dopamine D2-like receptor radioligands is quantitatively decreased, but it has not been known whether selected parts of the putamen are differentially affected depending upon the body part affected by dystonia. The radioligand [(18)F]spiperone binds predominantly to D2-like receptors in striatum. We hypothesized that the spatial location of [(18)F]spiperone binding within the putamen would differ in patients with dystonia limited to the hand versus the face, and we tested that hypothesis using positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. To address statistical and methodological concerns, we chose a straightforward but robust image analysis method. An automated algorithm located the peak location of [(18)F]spiperone binding within the striatum, relative to a brain atlas, in each of 14 patients with cranial dystonia and 8 patients with hand dystonia. The mean (left and right) |x|, y, and z coordinates of peak striatal binding for each patient were compared between groups by t test. The location of peak [(18)F]spiperone binding within the putamen differed significantly between groups (cranial dystonia z<hand dystonia z, p = 0.016). We conclude that in isolated focal dystonia, dopamine D2-like receptors are distributed differently in the putamen depending on the body part manifesting dystonia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Perlmutter JS, Tempel LW, Black KJ, Parkinson D, Todd RD (1997) MPTP induces dystonia and parkinsonism: Clues to the pathophysiology of dystonia. Neurology 49: 1432–1438. - PubMed
-
- Todd RD, Perlmutter JS (1998) Mutational and biochemical analysis of dopamine in dystonia: evidence for decreased dopamine D2 receptor inhibition. Molecular Neurobiology 16: 135–147. - PubMed
-
- Perlmutter JS, Mink JW (2004) Dysfunction of dopaminergic pathways in dystonia. Adv Neurol 94: 163–170. - PubMed
-
- Hallett M (2006) Pathophysiology of writer’s cramp. HumMov Sci 25: 454–463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

