Cripto-1 expression in glioblastoma multiforme
- PMID: 24521322
- PMCID: PMC8029290
- DOI: 10.1111/bpa.12131
Cripto-1 expression in glioblastoma multiforme
Abstract
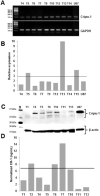
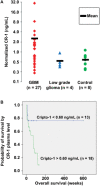
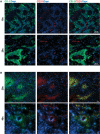
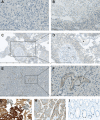
Human glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is an aggressive cancer with a very poor prognosis. Cripto-1 (CR-1) has a key regulatory role in embryogenesis, while in adult tissue re-expression of CR-1 has been correlated to malignant progression in solid cancers of non-neuronal origin. As CR-1 expression has yet to be described in cerebral cancer and CR-1 is regulated by signaling pathways dysregulated in GBM, we aimed to investigate CR-1 in the context of expression in GBM. The study was performed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), Western blotting, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and immunohistochemistry to analyze the blood and tissue from 28 GBM and 4 low-grade glioma patients. Within the patient cohort, we found high CR-1 protein levels in blood plasma to significantly correlate with a shorter overall survival. We identified CR-1 in different areas of GBM tissue, including perivascular tumor cells, and in endothelial cells. Collectively, our data suggest that CR-1 could be a prognostic biomarker for GBM with the potential of being a therapeutic target.
Keywords: CR-1; endothelial proliferation; glioblastoma multiforme; microvasculature; plasma biomarker; tumor niche.
© 2014 International Society of Neuropathology.
Figures
References
-
- Beier D, Hau P, Proescholdt M, Lohmeier A, Wischhusen J, Oefner PJ et al (2007) CD133(+) and CD133(−) glioblastoma‐derived cancer stem cells show differential growth characteristics and molecular profiles. Cancer Res 67:4010–4015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

