A probable crosstalk between Ca⁺², reactive oxygen species accumulation and scavenging mechanisms and modulation of protein kinase C activity during seed development in sunflower
- PMID: 24521818
- PMCID: PMC4091348
- DOI: 10.4161/psb.27900
A probable crosstalk between Ca⁺², reactive oxygen species accumulation and scavenging mechanisms and modulation of protein kinase C activity during seed development in sunflower
Abstract
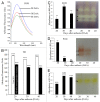
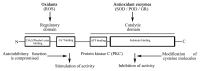
Seed development in sunflower involves a gradual dehydration and accumulation of oil bodies in the cells of developing cotyledons during transition from 30 to 40 DAA stage. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) content decreased with seed maturation. NO content and NO contributed by putative nitric oxide synthase, however, did not change markedly. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity exhibited a peak at 30 DAA stage, indicating its scavenging role at the mid-stage of seed development. H₂O₂ produced as a result of SOD action is subsequently scavenged primarily by elevation of GR activity. Significant temporal differences were evident in GR and POD activity during seed development. Protein kinase C (PKC) activity also showed modulation during early stages of embryo and seed development. Use of PKC-specific fluorescent probe, Fim-1, and PKC inhibitors (staurosporine and bisindoylmaleamide) provided evidence for increase in PKC activity at 40 DAA stage with an increase in protein concentration (50 to 200 µg). Endogenous calcium content also increased with seed maturation. Tissue homogenates from 40 DAA stage showed enhanced fluorescence due to Fim-1-PKC binding in presence of calcium ions and its lowering due to calcium chelating agent (BAPTA). Western blot analysis revealed an increase in the intensity of 2 bands representing PKC with the advancement of seed maturation and their further upregulation by calcium. Present findings, thus, provide new information on the biochemical regulation of seed development in sunflower, with evidence for a possible correlation between calcium, ROS, their scavenging enzymes and "conventional" PKC activity.
Keywords: Sunflower; calcium; glutathione reductase; peroxidase; protein kinase C; reactive oxygen species; seed development; superoxide dismutase.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Proteomic analysis of oil body membrane proteins accompanying the onset of desiccation phase during sunflower seed development.Plant Signal Behav. 2015;10(12):e1030100. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2015.1030100. Plant Signal Behav. 2015. PMID: 26786011 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric oxide and iron modulate heme oxygenase activity as a long distance signaling response to salt stress in sunflower seedling cotyledons.Nitric Oxide. 2016 Feb 29;53:54-64. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2016.01.003. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Nitric Oxide. 2016. PMID: 26778276
-
Melatonin and nitric oxide modulate glutathione content and glutathione reductase activity in sunflower seedling cotyledons accompanying salt stress.Nitric Oxide. 2016 Sep 30;59:42-53. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2016.07.001. Epub 2016 Jul 16. Nitric Oxide. 2016. PMID: 27432590
-
Biochemical mechanisms regulating salt tolerance in sunflower.Plant Signal Behav. 2019;14(12):1670597. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2019.1670597. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Plant Signal Behav. 2019. PMID: 31566062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of oxidants on calcium and sodium movement in healthy and diseased cardiac myocytes.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Oct;63:338-49. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.05.035. Epub 2013 Jun 1. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23732518 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic analysis of oil body membrane proteins accompanying the onset of desiccation phase during sunflower seed development.Plant Signal Behav. 2015;10(12):e1030100. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2015.1030100. Plant Signal Behav. 2015. PMID: 26786011 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association studies reveal novel QTLs for agronomic traits in soybean.Front Plant Sci. 2024 May 14;15:1375646. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1375646. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38807775 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling mechanisms and biochemical pathways regulating pollen-stigma interaction, seed development and seedling growth in sunflower under salt stress.Plant Signal Behav. 2021 Nov 2;16(11):1958129. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2021.1958129. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Plant Signal Behav. 2021. PMID: 34429013 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Quest AF, Bell RM. The regulatory region of protein kinase C γ. Studies of phorbol ester binding to individual and combined functional segments expressed as glutathione S-transferase fusion proteins indicate a complex mechanism of regulation by phospholipids, phorbol esters, and divalent cations. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:20000–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
