Caffeine and the analog CGS 15943 inhibit cancer cell growth by targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway
- PMID: 24521981
- PMCID: PMC4026075
- DOI: 10.4161/cbt.28018
Caffeine and the analog CGS 15943 inhibit cancer cell growth by targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway
Abstract
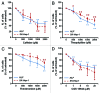
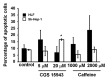
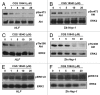
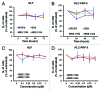
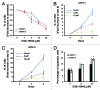
Caffeine is a naturally occurring methylxanthine that acts as a non-selective adenosine receptor antagonist. Epidemiological studies demonstrated habitual coffee drinking to be significantly associated with liver cancer survival. We aimed to investigate the effects of caffeine and its analog CGS 15943 on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and pancreatic cancer adenocarcinoma (PDAC). We demonstrate that caffeine and CGS 15943 block proliferation in HCC and PDAC cell lines by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt pathway. Importantly a kinase profiling assay reveals that CGS 15943 targets specifically the catalytic subunit of the class IB PI3K isoform (p110γ). These data give mechanistic insight into the action of caffeine and its analogs and they identify these compounds as promising lead compounds to develop drugs that can specifically target this PI3K isoform whose key role in cancer progression is emerging.
Keywords: CGS 15943; caffeine; hepatocellular carcinoma; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; phosphoinositide 3-kinase.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
