Effects of serum and plasma matrices on multiplex immunoassays
- PMID: 24522699
- PMCID: PMC4332596
- DOI: 10.1007/s12026-014-8491-6
Effects of serum and plasma matrices on multiplex immunoassays
Abstract
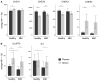
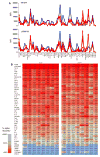
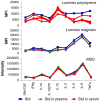
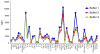
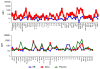
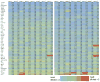
Multiplexed fluorescence or electrochemiluminescence immunoassays of soluble cytokines are commonly performed in the context of human serum or plasma, to look for disease biomarkers and to monitor the immune system in a simple and minimally invasive way. These assays provide challenges due to the complexities of the matrix (serum or plasma) and the presence of many cytokines near the limit of detection of the assay. Here, we compare the readout of matched serum and plasma samples, which are generally correlated. However, a subset of cytokines usually have higher levels in serum, and the non-specific background is significantly increased in serum versus plasma. Presumably as a result of this non-specific background, disease-related decreases in low-abundance cytokines can sometimes be detected in plasma but not in serum. We further show, through spike recovery experiments, that both serum and plasma inhibit the readout of many cytokines, with some variability between donors, but with serum causing greater inhibition than plasma in many cases. Standard diluents from different vendors can partially reverse this inhibition to varying degrees. Dilution of samples can also partly overcome the inhibitory effect of the matrix. We also show that dilution is nonlinear and differentially affects various cytokines. Together, these data argue that (1) plasma is a more sensitive matrix for detecting changes in certain low-abundance cytokines; (2) calculation of concentrations in serum or plasma matrices is inherently inaccurate; and (3) dilution of samples should not be assumed to be linear, i.e., all comparisons need to be made among similarly diluted samples.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Pang S, Smith J, Onley D, Reeve J, Walker M, Foy C. A comparability study of the emerging protein array platforms with established ELISA procedures. J Immunol Methods. 2005;302:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Breen EC, Reynolds SM, Cox C, Jacobson LP, Magpantay L, Mulder CB, Dibben O, Margolick JB, Bream JH, Sambrano E, Martinez-Maza O, Sinclair E, Borrow P, Landay AL, Rinaldo CR, Norris PJ. Multisite comparison of high-sensitivity multiplex cytokine assays. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2011;18:1229–42. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Maecker HT. Measuring human cytokines. In: O’Gorman MR, Donnenberg AD, editors. Handbook of human immunology. 2. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2008. pp. 517–40.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

