Anticonvulsants for alcohol dependence
- PMID: 24523233
- PMCID: PMC10585425
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008544.pub2
Anticonvulsants for alcohol dependence
Abstract
Background: Alcohol dependence is a major public health problem that is characterised by recidivism and a host of medical and psychosocial complications. Besides psychosocial interventions, different pharmacological interventions have been or currently are under investigation through Cochrane systematic reviews.
Objectives: The primary aim of the review is to assess the benefits/risks of anticonvulsants for the treatment of alcohol dependence.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Drugs and Alcohol Group Trials Register (October 2013), PubMed (1966 to October 2013), EMBASE (1974 to October 2013) and CINAHL (1982 to October 2013).
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and controlled clinical trials (CCTs) comparing anticonvulsants alone or in association with other drugs and/or psychosocial interventions versus placebo, no treatment and other pharmacological or psychosocial interventions.
Data collection and analysis: We used standard methodological procedures as expected by The Cochrane Collaboration.
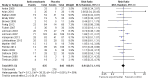
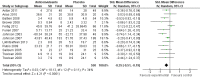
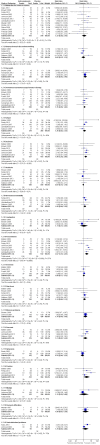
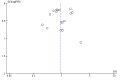
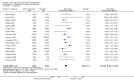
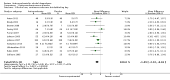
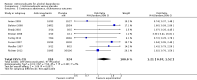
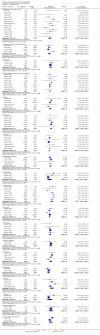
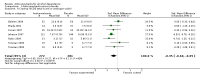
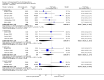
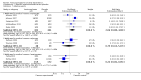
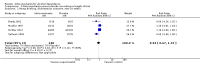
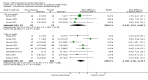
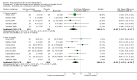
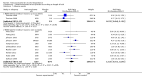
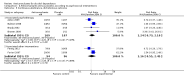
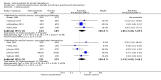
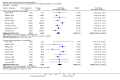
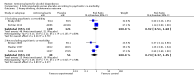
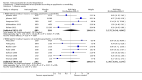
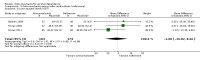
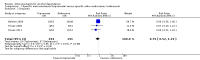
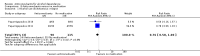
Main results: A total of 25 studies were included in the review (2641 participants). Most participants were male, with an average age of 44 years. Anticonvulsants were compared with placebo (17 studies), other medications (seven studies) and no medication (two studies). The mean duration of the trials was 17 weeks (range four to 52 weeks). The studies took place in the USA, Europe, South America, India and Thailand. Variation was reported in the characteristics of the studies, including their design and the rating instruments used. For many key outcomes, the risk of bias associated with unclear or unconcealed allocation and lack of blinding affected the quality of the evidence.Anticonvulsants versus placebo: For dropouts (16 studies, 1675 participants, risk ratio (RR) 0.94, 95% confidence interval (Cl) 0.74 to 1.19, moderate-quality evidence) and continuous abstinence (eight studies, 634 participants, RR 1.21, 95% Cl 95% 0.97 to 1.52, moderate-quality evidence), results showed no evidence of differences. Moderate-quality evidence suggested that anticonvulsants reduced drinks/drinking days (11 studies, 1126 participants, mean difference (MD) -1.49, 95% Cl -2.32 to -0.65) and heavy drinking (12 studies, 1129 participants, standardised mean difference (SMD) -0.35, 95% Cl -0.51 to -0.19). Moreover, withdrawal for medical reasons (12 studies, 1410 participants, RR 1.22, 95% Cl 0.58 to 2.56, moderate-quality evidence) showed no evidence of difference, but for specific adverse effects (nine studies, 1164 participants), two of 18 adverse event outcomes favoured placebo. The direction of results was confirmed by subgroup analyses for topiramate and partially for gabapentin and valproate.Anticonvulsants versus naltrexone: No evidence of difference was shown in dropout rates (five studies, 528 participants, RR 0.74, 95% CI 0.52 to 1.06), severe relapse rates (four studies, 427 participants, RR 0.69, 95% Cl 0.44 to 1.07) and continuous abstinence rates (five studies, 528 participants, RR 1.21, 95% Cl 0.99 to 1.49); anticonvulsants were associated with fewer heavy drinking days (three studies, 308 participants, MD -5.21, 95% Cl -8.58 to -1.83), more days to severe relapse (three studies, 244 participants, MD 11.88, 95% Cl 3.29 to 20.46) and lower withdrawal for medical reasons (three studies, 245 participants, RR 0.13, 95% Cl 0.03 to 0.58).
Authors' conclusions: At the current stage of research, randomised evidence supporting the clinical use of anticonvulsants to treat alcohol dependence is insufficient. Results are conditioned by heterogeneity and by the low number and quality of studies comparing anticonvulsants with other medications. The uncertainty associated with these results leaves to clinicians the need to balance possible benefits/risks of treatment with anticonvulsants versus other medications as supported by evidence of efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures

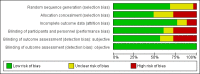
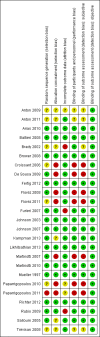






































Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Anton 2009 {published data only}
-
- Anton RF, Myrick H, Baros AM, Latham PK, Randall PK, Wright TM, et al. Efficacy of a combination of flumazenil and gabapentin in the treatment of alcohol dependence: relationship to alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2009;29:334‐42. - PubMed
Anton 2011 {published data only}
Arias 2010 {published data only}
Baltieri 2008 {published data only}
-
- Baltieri DA, Daró FR, Ribeiro PL, Andrade AG. Comparing topiramate with naltrexone in the treatment of alcohol dependence. Addiction 2008;103:2035‐44. - PubMed
Brady 2002 {published data only}
-
- Brady KT, Myrick H, Henderson S, Coffey SF. The use of divalproex in alcohol relapse prevention: a pilot study. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2002;67:323‐30. - PubMed
Brower 2008 {published data only}
Croissant 2006 {published data only}
-
- Croissant B, Diehl A, Klein O, Zambrano S, Nakovics H, Heinz A, et al. A pilot study of oxcarbazepine versus acamprosate in alcohol‐dependent patients. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2006;30:630‐5. - PubMed
De Sousa 2008 {published data only}
-
- Sousa AA, Sousa J, Kapoor H. An open randomized trial comparing disulfiram and topiramate in the treatment of alcohol dependence. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2008;34:460‐3. - PubMed
Fertig 2012 {published data only}
-
- Fertig JB, Ryan ML, Falk DE, Litten RZ, Mattson ME, Ransom J, et al. NCIG 002 Study Group. A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial assessing the efficacy of levetiracetam extended‐release in very heavy drinking alcohol‐dependent patients. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2012;36:1421‐30. - PMC - PubMed
Florez 2008 {published data only}
-
- Flórez G, García‐Portilla P, Alvarez S, Saiz PA, Nogueiras L, Bobes J. Using topiramate or naltrexone for the treatment of alcohol‐dependent patients. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2008;32:1251‐9. - PubMed
Florez 2011 {published data only}
-
- Florez G, Saiz PA, Garcia‐Portilla P, Alvarez S, Nogueiras L, Bobes J. Topiramate for the treatment of alcohol dependence: comparison with naltrexone. European Addiction Research 2011;17:29‐36. - PubMed
Furieri 2007 {published data only}
-
- Furieri FA, Nakamura‐Palacios EM. Gabapentin reduces alcohol consumption and craving: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2007;68:1691‐700. - PubMed
Johnson 2003 {published data only}
-
- Johnson BA, Ait‐Daoud N, Akhtar FZ, Ma JZ. Oral topiramate reduces the consequences of drinking and improves the quality of life of alcohol‐dependent individuals: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of General Psychiatry 2004;61:905‐12. - PubMed
-
- Johnson BA, Ait‐Daoud N, Bowden CL, DiClemente CC, Roache JD, Lawson K, et al. Oral topiramate for treatment of alcohol dependence: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2003;361::1677‐85. - PubMed
-
- Ma JZ, Ait‐Daoud N, Johnson BA. Topiramate reduces the harm of excessive drinking: implications for public health and primary care. Addiction 2006;101:1561‐8. - PubMed
Johnson 2007 {published data only}
-
- Johnson BA, Rosenthal N, Capece JA, Wiegand F, Mao L, Beyers K, et al. Topiramate for Alcoholism Advisory Board, Topiramate for Alcoholism Study Group. Improvement of physical health and quality of life of alcohol‐dependent individuals with topiramate treatment: US multisite randomized controlled trial. Archives of Internal Medicine 2008;168:1188‐99. - PubMed
-
- Johnson BA, Rosenthal N, Capece JA, Wiegand F, Mao L, Beyers K, et al. Topiramate for Alcoholism Advisory Board, Topiramate for Alcoholism Study Group. Topiramate for treating alcohol dependence: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2007;298:1641‐51. - PubMed
Kampman 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Kampman KM. A Phase II, Randomized, Double‐blind, Placebo‐Controlled, Pilot Trial of Topiramate for Alcohol and Comorbid Cocaine Dependence. ClinicalTrials.gov 2005.
Likhitsathian 2013 {published data only}
-
- Likhitsathian S, Uttawichai K, Booncharoen H, Wittayanookulluk A, Angkurawaranon C, Srisurapanont M. Topiramate treatment for alcoholic outpatients recently receiving residential treatment programs: a 12‐week, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2013;133:440‐6. - PubMed
Martinotti 2007 {published data only}
-
- Martinotti G, Nicola M, Romanelli R, Andreoli S, Pozzi G, Moroni N, et al. High and low dosage oxcarbazepine versus naltrexone for the prevention of relapse in alcohol‐dependent patients. Human Psychopharmacology 2007;22:149‐56. - PubMed
-
- Martinotti G, Romanelli R, Nicola M, Reina D, Mazza M, Janiri L. Oxcarbazepine at high dosages for the treatment of alcohol dependence. American Journal of Addiction 2007;16:247‐8. - PubMed
Martinotti 2010 {published data only}
-
- Martinotti G, Nicola M, Tedeschi D, Andreoli S, Reina D, Pomponi M, et al. Pregabalin versus naltrexone in alcohol dependence: a randomised, double‐blind, comparison trial. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2010;24:1367‐74. - PubMed
Mueller 1997 {published data only}
-
- Mueller TI, Stout RL, Rudden S, Brown RA, Gordon A, Solomon DA, et al. A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled pilot study of carbamazepine for the treatment of alcohol dependence. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 1997;21:86‐92. - PubMed
Paparrigopoulos 2010 {published data only}
-
- Paparrigopoulos T, Tzavellas E, Karaiskos D, Malitas P, Liappas I. An open pilot study of tiagabine in alcohol dependence: tolerability and clinical effects. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2010;24:1375‐80. - PubMed
Paparrigopoulos 2011 {published data only}
Richter 2012 {published data only}
-
- Richter C, Effenberger S, Bschor T, Bonnet U, Haasen C, Preuss UW, et al. Efficacy and safety of levetiracetam for the prevention of alcohol relapse in recently detoxified alcohol‐dependent patients: a randomized trial. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2012;32:558‐62. - PubMed
Rubio 2009 {published data only}
-
- Rubio G, Martínez‐Gras I, Manzanares J. Modulation of impulsivity by topiramate: implications for the treatment of alcohol dependence. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2009;29:584‐9. - PubMed
Salloum 2005 {published data only}
-
- Salloum IM, Cornelius JR, Daley DC, Kirisci L, Himmelhoch JM, Thase ME. Efficacy of valproate maintenance in patients with bipolar disorder and alcoholism: a double‐blind placebo‐controlled study. Archives of General Psychiatry 2005;62:37‐45. - PubMed
Trevisan 2008 {published data only}
-
- Trevisan LA, Ralevski E, Keegan K, Oville A, Vuppalapati D, Gonzalez G, et al. Alcohol detoxification and relapse prevention using valproic acid versus gabapentin in alcohol‐dependent patients. Addictive Disorders and Their Treatment 2008;7:119.
References to studies excluded from this review
Karam‐Hage 2003 {published data only}
Knapp 2010 {published data only}
Le Strat 2012 {published data only}
-
- Strat Y. Levetiracetam in the treatment of alcohol dependence: toward the end of the story?. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2012;36:1309‐10. - PubMed
Miranda 2008 {published data only}
-
- Miranda R Jr, MacKillop J, Monti PM, Rohsenow DJ, Tidey J, Gwaltney C, et al. Effects of topiramate on urge to drink and the subjective effects of alcohol: a preliminary laboratory study. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2008;32:489‐97. - PubMed
Mitchell 2012 {published data only}
-
- Mitchell JM, Grossman LE, Coker AR, Messing RO. The anticonvulsant levetiracetam potentiates alcohol consumption in non‐treatment seeking alcohol abusers. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2012;32:269‐72. - PubMed
Myrick 2007 {published data only}
-
- Myrick H, Anton R, Voronin K, Wang W, Henderson S. A double‐blind evaluation of gabapentin on alcohol effects and drinking in a clinical laboratory paradigm. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2007;31:221‐7. - PubMed
Narayana 2008 {published data only}
Schacht 2013 {published data only}
References to studies awaiting assessment
Bajovic 2012 {published data only}
-
- Bajovic B, Zivkovic N, Djokic G, Pavicevic D. Oxcarbazepine, topiramate and lamotrigine in the treatment of alcohol craving. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2012;22:S65‐6.
De Vita 2012 {published data only}
-
- Vita O, Martinotti G, Nicola M, Tedeschi D, Hatzigiakoumis DS, Monetta M, et al. Topiramate at low dosage vs. placebo in alcohol dependence. European Psychiatry 2012;27:1.
MacKillop 2012 {published data only}
-
- MacKillop J, Monti PM, Tidey J, Swift RM, Ray LA, Miranda R. Behavioral economic analysis of topirmate's effects on motivation for alcohol. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2012;36:247A.
Mason 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Mason BJ. Gabapentin Treatment of Alcohol Dependence. ClinicalTrials.gov 2006.
-
- Mason BJ. Gabapentin in alcoholism: from laboratory study to clinical trial. Basic Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology 2010:107.
-
- Mason BJ. Human laboratory and clinical trial evidence for gabapentin treatment of alcohol dependence. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2010;34:64A.
Miranda 2011 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Miranda R, MacKillop J, Meehan J, Justus A, Tidey J, Ramirez J, et al. Biobehavioral effects of topiramate among heavy drinkers. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 2011; Vol. 35:21A.
Rubio 2002 {published data only}
-
- Rubio G, Ponce G, Ortiz S, Oliva JM, Manzanares J, Jimenez‐Arriero MA, et al. Comparison between gabapentine and acamprosate in the treatment of alcohol dependent patients. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2002;12:398.
References to ongoing studies
Ait‐Daoud 2010 {unpublished data only}
-
- Ait‐Daoud N, Anthenelli RM, Cinciripini PM, Johnson BA. New Pharmacotherapy for Alcohol and Co‐morbid Disorders. ClinicalTrials.gov 2010.
Anthenelli 2008 {unpublished data only}
-
- Anthenelli R, Heffner JL, Nolting S. Topiramate to Aid Smoking Cessation in Recovering Alcohol Dependent Men. ClinicalTrials.gov 2008.
Batki 2010 {unpublished data only}
-
- Batki LS. Topiramate Treatment of Alcohol Use Disorders in Veterans With Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): A Pilot Controlled Trial of Augmentation Therapy. ClinicalTrials.gov 2010.
Beresford 2011 {unpublished data only}
-
- Beresford TP. A Double Blind Trial Of Divalproex Sodium For Affective Lability And Alcohol Use Following Traumatic Brain Injury. ClinicalTrials.gov 2011.
Ciraulo 2009 {unpublished data only}
-
- Ciraulo DA, Sarid‐Segal O, Afshar M. A Double‐Blind, Placebo‐Controlled, Parallel Group Design Trial of: Levetiracetam, Zonisamide, Topiramate, and Placebo Control for the Treatment of Alcohol Dependent Subjects. ClinicalTrials.gov 2009.
Del Bello 2007 {unpublished data only}
-
- DelBello M. Quetiapine Plus Topiramate or Placebo for Bipolar Mania and Alcohol Use in Adolescents & Young Adults. ClinicalTrials.gov 2007.
Fischer 2011 {unpublished data only}
-
- Fischer BA. A 14‐week Randomized, Placebo‐controlled Study of Topiramate for Alcohol Use Disorders in Veterans With Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. ClinicalTrials.gov 2011.
Frye 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Frye MA. An Evaluation of Divalproex vs. Olanzapine for Alcohol Abuse Relapse Prevention in Patients With Bipolar Disorder. ClinicalTrials.gov 2005.
Johnson 2000 {unpublished data only}
-
- Johnson BA, Ait‐Daoud N. Combining Medications: Treatment for Alcoholism. ClinicalTrials.gov 2000.
Johnson 2007 b {unpublished data only}
-
- Johnson B, Ait‐Daoud N. Novel Pharmacotherapy for Dual Dependence. ClinicalTrials.gov 2007.
Jorge 2011 {unpublished data only}
-
- Jorge RE. Treatment Strategy for Alcohol Use Disorders in Veterans With TBI. ClinicalTrials.gov 2011.
Kampman 2011 {unpublished data only}
-
- Kampman KM. A Phase II, Double‐Blind, Placebo‐Controlled, Pilot Trial of Vigabatrin for the Treatment of Cocaine and Alcohol Dependence. ClinicalTrials.gov 2011.
Kranzler 2008 {unpublished data only}
-
- Kranzler HR, Covault J, Arias A, Oncken C, Tennen H, Gelernter J, Armeli S, Drazinic C, Chamberlain S, Levine E, Jensen K, Lieberman R. Topiramate Treatment of Problem Drinkers. ClinicalTrials.gov 2008.
Mariani 2010 {unpublished data only}
-
- Mariani J. Gabapentin for Abstinence Initiation in Alcohol Dependence. ClinicalTrials.gov 2010.
Mason 2009 {unpublished data only}
-
- Mason BJ. Duloxetine Versus Pregabalin for Alcohol Dependence. ClinicalTrials.gov 2009.
Messing 2008 {unpublished data only}
-
- Messing RO, Mitchell JM. Placebo‐Controlled Crossover Trial of Levetiracetam on Ethanol Intake. ClinicalTrials.gov 2008.
Ostacher 2007 {unpublished data only}
-
- Ostacher MJ. Adjunctive Topiramate for Treatment of Alcohol Dependence in Patients With Bipolar Disorder. ClinicalTrials.gov 2007.
Petrakis 2007 {unpublished data only}
-
- Petrakis IL. The Use of Anticonvulsants for Treatment of Patients With Alcohol Dependence and Post Traumatic Stress Disorder. ClinicalTrials.gov 2007.
Ralevski 2007 {unpublished data only}
-
- Ralevski E. Topiramate for Treatment of Patients With Borderline Personality Disorder and Alcohol Dependence. ClinicalTrials.gov 2007.
Schaefer 2008 {unpublished data only}
-
- Schaefer M. Efficacy and Safety of Levetiracetam in Prevention of Alcohol Relapse in Recently Detoxified Alcohol Dependent Patients. ClinicalTrials.gov 2008. - PubMed
South Carolina 2001 {unpublished data only}
-
- Alcohol Research Center—Treatment and Implications. ClinicalTrials.gov 2001.
Tolliver 2009 {unpublished data only}
-
- Tolliver BK, Brady KT. A Double‐Blind, Placebo‐Controlled Trial of Lamotrigine In Individuals With Bipolar Disorder and Comorbid Alcohol Dependence. ClinicalTrials.gov 2009.
Additional references
Amato 2010
Anderson 2006
-
- Anderson P, Baumberg B. Alcohol in Europe: A Report for the European Commission. London: Institute of Alcohol Studies, 2006.
Anton 1995
-
- Anton RF, Moak DH, Latham P. The obsessive compulsive drinking scale: a self‐rated instrument for the quantification of thoughts about alcohol and drinking behavior. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 1995;19:92‐9. - PubMed
Anton 1996
-
- Anton RF, Moak DH, Latham PK. The obsessive compulsive drinking scale: a new method of assessing outcome in alcoholism treatment studies. Archives of General Psychiatry 1996;53:225‐31. - PubMed
Anton 2006
-
- Anton RF, O'Malley SS, Ciraulo DA, Cisler RA, Couper D, Donovan DM, et al. COMBINE Study Research Group. Combined pharmacotherapies and behavioral interventions for alcohol dependence: the COMBINE study: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of the American Medical Association 2006;295:2003‐17. - PubMed
APA 1987
-
- American Psychiatric Association. DSM‐III‐R Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 3rd Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1987.
APA 1994
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1994.
APA 2000
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Text Revision. 4th Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 2000.
Arbaizar 2010
-
- Arbaizar B, Diersen‐Sotos T, Gómez‐Acebo I, Llorca J. Topiramate in the treatment of alcohol dependence: a meta‐analysis. Actas Espanolas de Psiquiatria 2010;38:8‐12. - PubMed
Bastien 2001
-
- Bastien CH, Vallieres A, Morin CM. Validation of the Insomnia Severity Index as an outcome measure for insomnia research. Sleep Medicine 2001;2:297‐307. - PubMed
Bech 1979
-
- Bech P, Bolwig TG, Kramp P, Rafaelsen OJ. The Bech‐Rafaelsen Mania Scale and the Hamilton Depression Scale. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1979;59:420‐30. - PubMed
Beck 1961
-
- Beck A, Ward C, Mendelson M, Mock J, Erbaugh J. An inventory for measuring depression. Archives of General Psychiatry 1961;4:561. - PubMed
Beck 1988
-
- Beck AT, Epstein N, Brown G, Steer RA. An inventory for measuring clinical anxiety: psychometric properties. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1988;56:893‐7. - PubMed
Bohn 1995 a
-
- Bohn MJ, Babor TF, Kranzler HR. The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT): validation of a screening instrument for use in medical settings. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs 1995;56:423‐32. - PubMed
Bohn 1995 b
-
- Bohn MJ, Krahn DD, Staehler BA. Development and initial validation of a measure of drinking urges in abstinent alcoholics. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 1995;19:600‐6. - PubMed
Bohn 1996
-
- Bohn MJ, Barton BA, Barron KE. Psychometric properties and validity of the obsessive‐compulsive drinking scale. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 1996;20:817‐23. - PubMed
Buss 1957
-
- Buss AH, Durkee A. An inventory for assessing different kinds of hostility. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1957;21:343‐9. - PubMed
Buysse 1989
-
- Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF, Monk TH, et al. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Research 1989;28:193‐213. - PubMed
Carroll 1987
-
- Carroll KM. Enhancing retention in clinical trials of psychosocial treatments: practical strategies. Beyond the therapeutic alliance: keeping the drug‐dependent individual in treatment. NIDA Research Monograph. Vol. 165, National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), 1997. - PubMed
Carroll 1996 a
-
- Carroll K, O’Malley S. Compliance Enhancement: A Manual for the Psychopharmacotherapy of Alcohol Dependence. New Haven, CT: Yale University, 1996.
Carroll 1996 b
-
- Carroll KM. Relapse prevention as a psychosocial treatment: a review of controlled clinical trials. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology 1996;4:46‐54.
Cavanna 2010
-
- Cavanna AE, Ali F, Rickards HE, McCorry D. Behavioral and cognitive effects of anti‐epileptic drugs. Discovery Medicine 2010;9:138‐44. - PubMed
Chase 2005
-
- Chase V, Neild R, Sadler CW, Batey RG. The medical complications of alcohol use: understanding mechanisms to improve management. Drug and Alcohol Review 2005;24:253‐65. - PubMed
Coccaro 1991
-
- Coccaro EF, Harvey PD, Kupsaw‐Lawrence E, Herbert JL, Bernstein DP. Development of neuropharmacologically based behavioral assessments of impulsive aggressive behavior. Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience 1991;3:S44‐51. - PubMed
Conners 1995 [Computer program]
-
- Conners C. Continuous Performance Test Computerprogram 3.0: User's Manual.. Toronto, Ontario, Canada: Multi‐Health Systems, Inc, 1995.
Conroy 2006
Cooney 1990
-
- Cooney NL, Kadden RM, Litt MD. A comparison of methods for assessing sociopathy in male and female alcoholics. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs 1990;51:42‐8. - PubMed
Crits‐Christoph 1999
-
- Crits‐Christoph P, Siqueland L, Blaine J, Frank A, Luborsky L, Onken LS, et al. Psychosocial treatments for cocaine dependence: National Institute on Drug Abuse Collaborative Cocaine Treatment Study. Archives of General Psychiatry 1999;56:493‐502. - PubMed
Czapinski 2005
-
- Czapinski P, Blaszczyk B, Czuczwar SJ. Mechanisms of action of antiepileptic drugs. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry 2005;5:3‐14. - PubMed
Daley 1993
-
- Daley DC, Marlatt GA. Relapse prevention: cognitive and behavioral interventions. In: Lowinson JH, Ruiz P, Millman BR, Langrod JC editor(s). Substance Abuse, A Comprehensive Textbook. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins, 1993:533‐42.
Daley 1994
-
- Daley DC, Thase ME. Dual Disorders Recovery Counseling. Independence, Mo: Independence Press, 1994.
Davidson 1989
-
- Davidson R, Bunting B, Raistrick D. The homogeneity of the alcohol dependence syndrome: a factorial analysis of the SADD questionnaire. British Journal of Addiction 1989;84:907‐15. - PubMed
Davis 2008
-
- Davis L, Uezato A, Newell JM, Frazier E. Major depression and comorbid substance use disorders. Current Opinion on Psychiatry 2008;21:14‐8. - PubMed
De Sousa 2010
-
- Sousa A. The role of topiramate and other anticonvulsants in the treatment of alcohol dependence: a clinical review. CNS and Neurological Disorders Drug Targets 2010;9:45‐9. - PubMed
Derogatis 1977
-
- Derogatis LR. SCL‐90‐R: Administration, Scoring, and Procedure Manual I. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Clinical Psychometrics Research Unit, 1977.
DiChiara 1988
Drevets 2001
-
- Drevets WC, Gautier C, Price JC, Kupfer DJ, Kinahan PE, Grace AA, et al. Amphetamine‐induced dopamine release in human ventral striatum correlates with euphoria. Biological Psychiatry 2001;49:81‐96. - PubMed
Efron 1971
-
- Efron B. Forcing a sequential experiment to be balanced. Biometrika 1971;58:403‐17.
Endicott 1976
-
- Endicott J, Spitzer RL, Fleiss JL, Cohen J. The Global Assessment Scale: a procedure for measuring overall severity of psychiatric disturbance. Archives of General Psychiatry 1976;33:766‐71. - PubMed
EuroQuoL 1990
-
- EuroQoL Group. EuroQoL—a new facility for the measurement of health–related quality of life. Health Policy 1990;16:199‐208. - PubMed
Fangeström 1978
-
- Fagerström KO. Measuring degrees of physical dependence to tobacco smoking with reference to individualization of treatment. Addiction Behavior 1978;3:235‐41. - PubMed
Feinn 2003
-
- Feinn R, Tennen H, Kranzler HR. Psychometric properties of the short index of problems as a measure of recent alcohol‐related problems. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2003;27:1436‐41. - PubMed
First 1994
-
- First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JBW. Structured clinical interview for DSM‐IV axis I disorders—patient edition (SCID‐I/P,Version 2.0). Structured Clinical Interview for DSM‐IV Axis I Disorders—Patient Edition (SCID‐I/P, Version 2.0). New York: New York State Psychiatric Institute, Biometrics Research Department, 1994.
First 1995
-
- First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JBW. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM‐IV. Patient. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Press, 1995.
First 1997
-
- First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JBW. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM‐IV Axis I Disorders—Patient Edition (SCID‐I/P, Version 2.0). Structured Clinical Interview for DSM‐IV Axis I Disorders—Patient Edition (SCID‐I/P, Version 2.0). New York: New York State Psychiatric Institute, Biometrics Research Department, 1997.
Flannery 1999
-
- Flannery BA, Volpicelli JR, Pettinati HM. Psychometric properties of thePenn Alcohol Craving Scale. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 1999;23:1289‐95. - PubMed
Flannery 2002
-
- Flannery BA, Allen JP, Pettinati HM, et al. Using acquired knowledge and new technologies in alcoholism treatment trials. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2002;26:423‐9. - PubMed
Folstein 1975
-
- Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. "Mini‐mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatry Research 1975;12:189‐98. - PubMed
Fox 2003
-
- Fox C, Loughlin P, Cook C. Disulfiram for alcohol dependence. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2003, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004331] - DOI
Gordon 1988
-
- Gordon M, Mettelman BB. The assessment of attention: I.Standardization and reliability of a behavior‐based measure. Journal of Clinical Psychology 1988;44:682‐90. - PubMed
Guadagnoli 1989
-
- Guadagnoli E, Mor V. Measuring cancer patients’ affect: revision and psychometric properties of the profile of mood states (POMS). Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1989;11:150‐4.
Guy 1976
-
- Guy W. ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology. Revised. DHEW pub. No. (ADM) 76‐338. Rockville, MD: National Institute of Mental Health, 1976.
Halikas 1991
-
- Halikas JA, Kuhn KL, Crosby R, Carlson G, Crea F. The measurement of craving in cocaine patients using the Minnesota Cocaine Craving Scale. Comprehensive Psychiatry 1991;32:22‐7. - PubMed
Hamilton 1959
-
- Hamilton M. The assessment of anxiety states by rating. British Journal of Psychiatry 1959;32:50‐5. - PubMed
Hamilton 1960
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration. www.cochrane‐handbook.org 2011.
Horn 1983
-
- Horn JL, Wanberg KW, Foster FM. The Alcohol Use Inventory. Baltimore, MD: Psych Systems, 1983.
Hughes 1980
-
- Hughes PH, Venulet J, Khant U, Medina Mora ME, Navaratnam V, Poshyachinda V, et al. Core Data for Epidemiological Studies on Non Medical Drug Users. Geneva: WHO Offset Publication, 1980. - PubMed
Janca 1996
-
- Janca A, Kastrup M, Katschnig H, López–Ibor JJ, Mezzich JE, Sartorius N. The World Health Organization Short Disability Assessment Schedule (WHO DAS–S): a tool for the assessment of difficulties in selected areas of functioning of patients with mental disorders. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology 1996;31:349‐54. - PubMed
Jenkins 1988
-
- Jenkins CD, Stanton BA, Niemcryk SJ, Rose RM. A scale for the estimation of sleep problems in clinical research. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1988;41:313‐21. - PubMed
Johns 1991
-
- Johns MW. A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep 1991;14:540‐5. - PubMed
Johnson 2003b
-
- Johnson BA, DiClemente CC, Ait‐Daoud N, Stoks SM. Brief Behavioral Compliance Enhancement Treatment (BBCET) manual. In: Johnson BA, Ruiz P, Galanter M editor(s). Handbook of Clinical Alcoholism Treatment. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2003:282‐301.
Johnson 2005
-
- Johnson BA, Ait‐Daoud N, Roache JD. The COMBINE SAFTEE: a structured instrument for collecting adverse events adapted for clinical studies in the alcoholism field. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs 2005;15 Suppl:157‐67. - PubMed
Kadden 1992
-
- Kadden R, Carroll KM, Donovan D, Cooney N, Monti P, Abrams D, Litt M, Hester R. Cognitive Behavioral Coping Skills Manual. Washington, DC: U.S. Governmmet Printing Office, 1992.
Kadden 1995
-
- Kadden R, Carroll K, Donovan D, Cooney M, Monti P, Abrams D, et al. Cognitive‐Behavioral Coping Skill Therapy Manual. Project MATCH Monograph Series. National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, 1995.
Kampman 1998
-
- Kampman KM, Volpicelli JR, McGinnis DE, Alterman AI, Weinieb RM, D’Angelo LD, et al. Reliability and validity of the cocaine selective severity assessment. Addiction Behavior 1998;23:449‐61. - PubMed
Kenna 2009
-
- Kenna GA, Lomastro TL, Schiesl A, Leggio L, Swift RM. Review of topiramate: an antiepileptic for the treatment of alcohol dependence. Current Drug Abuse Review 2009;2:135‐42. - PubMed
Kokkevi 1995
-
- Kokkevi A, Hartgers C. European adaptation of a multidimensional assessment instrument for drug and alcohol dependence. European Addiction Research 1995;1:208‐10.
Kongsakon 2000
-
- Kongsakon, Silpakit C. Thai version of the medical outcome study 36 items short form health survey: an instrument for measuring clinical results in mental disorder patients. Ramathibodi Medical Journal 2000;23:8‐19.
Koob 1997
-
- Koob GF, Nestler EJ. The neurobiology of drug addiction. Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 1997;9:482‐97. - PubMed
Landmark 2007
-
- Landmark CJ. Targets for antiepileptic drugs in the synapse. Medical Science Monitor 2007;13:RA 1‐7. - PubMed
Lefebvre 2011
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J, on behalf of the Cochrane Information Retrieval Methods Group. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Leone 2010
Levine 1986
-
- Levine J, Schooler NR. SAFTEE: a technique for the systematic assessment of side effects in clinical trials. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1986;22:343‐81. - PubMed
Lingjaerde 1987
-
- Lingjaerde O, Ahlfors UG, Bech P, Dencker SJ, Elgen K. The UKU side effect rating scale. A new comprehensive rating scale for psychotropic drugs and a cross‐sectional study of side effects in neuroleptic‐treated patients. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1987;334 Suppl:1‐100. - PubMed
Logan 1994
-
- Logan J. On the ability to inhibit thought and action: a user's guide to the stop signal paradigm. In: Dagenbach D, Carr TH editor(s). Inhibitory Processes in Attention, Memory and Language. San Diego: Academic Press, 1994.
Loranger 1994
-
- Loranger AW, Sartorius N, Andreoli P, Berger P, Buchheim SM, Channabasavanna SM, et al. The international personality disorder examination. Archives of General Psychiatry 1994;51:215‐24. - PubMed
Lubman 2007
-
- Lubman DI, Allen NB, Rogers N, Cementon E, Bonomo Y. The impact of co‐occurring mood and anxiety disorders among substance‐abusing youth. Journal of Affective Disorders 2007;103:105‐12. - PubMed
Mannelli 2007
-
- Mannelli P, Pae CU. Medical comorbidity and alcohol dependence. Current Psychiatry Reports 2007;9:217‐24. - PubMed
McLellan 1980
-
- McLellan AT, Luborsky L, Woody GE, O’Brien CP. An improved diagnostic evaluation instrument for substance abuse patients: the Addiction Severity Index. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1980;168:26‐33. - PubMed
McLellan 1985
-
- McLellan AT, Luborsky L, Cacciola J, Griffith JE, McGahan P, O’Brien CP. Guide to the Addiction Severity Index: Background Administration and Field Testing Results. Rockville, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, 1985.
McLellan 1992
-
- McLellan AT, Kushner H, Metzger D, Peters R, Smith I, Grissom G, et al. The fifth edition of the addiction severity index. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 1992;9:199‐213. - PubMed
McNair 1971
-
- McNair DM, Lorr M, Droppleman LF. Manual for the Profile of Mood States. San Diego, CA: Educational & Industrial Testing Service, 1971.
Miller 1984
-
- Miller WR, Marlatt GA. Manual for the Comprehensive Drinker Profile. Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources, 1984.
Miller 1995
-
- Miller W. The Drinker Inventory of Consequences (DrInC): an instrument for assessing adverse consequences of alcohol abuse. In: Mattson M, Marshall LA editor(s). NIAAA Project MATCH Monograph Series. Vol. 4, Bethesda, MD : National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, 1995:1‐94.
Miller 1996
-
- Miller WR. Form 90: A structured assessment interview for drinking and related behaviors test manual. In: Mattson ME, Marshall LA editor(s). NIAAA Project Match Monograph Series. Vol. 5, Rockville, MD: National Institute on Alcoholism and Alcohol Abuse, 1996.
Miller 2004
-
- Miller WR. Combined Behavioral Intervention Manual: A Clinical Research Guide for Therapists Treating People With Alcohol Abuse and Dependence. Vol. 1, Bethesda, MD: National Institute of Health, 2004.
Minozzi 2010
Moak 1998
-
- Moak DH, Anton RF, Latham PK. Further validation of the obsessive‐compulsive drinking scale (OCDS): relationship to alcoholism severity. American Journal of Addiction 1998;7:14‐23. - PubMed
Moher 2001
-
- Moher D, Jones A, Lepage L, CONSORT Group (Consolidated Standards for Reporting of Trials). The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel‐group randomized trials. Journal of the American Medical Association 2001;285:1992‐5. - PubMed
Montgomery 1979
-
- Montgomery SA, Asberg M. A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change. British Journal of Psychiatry 1979;134:382‐9. - PubMed
Monti 1989
-
- Monti PM, Abrams DB, Kadden RM, Cooney NL. Treating Alcohol Dependence: A Coping Skills Training Guide. New York: Guildford Press, 1989.
Morin 1993
-
- Morin CM. Insomnia: Psychological Assessment and Management. New York: Guilford, 1993.
Morisky 1986
-
- Morisky DE, Green LW, Levine DM. Concurrent and predictive validity of a self–reported measure of medication adherence. Medical Care 1986;24:67‐74. - PubMed
Mottola 1993
-
- Mottola CA. Measurement strategies: the visual analogue scale. Decubitus 1993;6:56‐8. - PubMed
Nich 2002
Olsmed 2008
-
- Olmsted CL, Kockler DR. Topiramate for alcohol dependence. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2008;42:1475‐80. - PubMed
Patton 1995
-
- Patton JH, Stanford MS, Barratt ES. Factor structure of the Barratt Impulsivity Scale. Journal of Clinical Psychology 1995;51:768‐74. - PubMed
Post 1986
-
- Post RM, Rubinow DR, Ballenger JC. Conditioning and sensitisation in the longitudinal course of affective illness. British Journal of Psychiatry 1986;149:191‐201. - PubMed
Project MATCH Research Group 1997
-
- Project MATCH Research Group. Matching alcoholism treatments to client heterogeneity: project MATCH posttreatment drinking outcomes. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs 1997;58:7‐29. - PubMed
Raistrick 1983
-
- Raistrick D, Dunbar G, Davidson R. Development of a questionnaire to measure alcohol dependence. British Journal of Addiction 1983;78:89‐95. - PubMed
Rehm 2009
-
- Rehm J, Mathers C, Popova S, Thavorncharoensap M, Teerawattananon Y, Patra J. Global burden of disease and injury and economic cost attributable to alcohol use and alcohol‐use disorders. Lancet 2009;373:2223‐33. - PubMed
Rehm 2011
Roberts 1999
-
- Roberts JS, Anton RF, Latham PK, Moak DH. Factor structure and predictive validity of the Obsessive Compulsive Drinking Scale. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 1999;23:1484‐91. - PubMed
Robins 1988
-
- Robins LN, Wing J, Wittchen HU, Helzer JE, Babor TF, Burke J, et al. The Composite International Diagnostic Interview. An epidemiologic Instrument suitable for use in conjunction with different diagnostic systems and in different cultures. Archives of General Psychiatry 1988;45:1069‐77. - PubMed
Rollnik 1992
-
- Rollnick S, Heather N, Gold R, Hall W. Development of a short ‘readiness to change’ questionnaire for use in brief, opportunistic interventions among excessive drinkers. British Journal of Addiction 1992;87:743‐54. - PubMed
Rösner 2010
Rösner 2010 a
Sheehan 1998
-
- Sheehan DV, Lecrubier Y, Sheehan KH, et al. The Mini‐International Neuropsychiatric Interview (M.I.N.I.): the development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM‐IV and ICD‐10. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1998;59(Suppl 20):22‐33. - PubMed
Shinn 2010
Skinner 1982
-
- Skinner HA, Allen BA. Alcohol dependence syndrome: measurement and validation. Journal of Abnormal Psychology 1982;91:199‐209. - PubMed
Skinner 1984
-
- Skinner HA, Horn JL. Alcohol Dependence Scale: Users Guide. Toronto, Canada: Addiction Research Foundation, 1984.
Sobell 1979
-
- Sobell LC, Maisto SA, Sobell MB, et al. Reliability of alcohol abusers’ self‐reports of drinking behavior. Behavioral Research and Therapy 1979;17:157‐60. - PubMed
Sobell 1988
-
- Sobell LC, Sobell MB, Leo GI, Cancilla A. Reliability of a timeline method: assessing normal drinkers’ reports of recent drinking and a comparative evaluation across several populations. British Journal of Addiction 1988;83:393‐402. - PubMed
Sobell 1992
-
- Sobell LC, Sobell MB. Timeline follow‐back: a technique for assessing self‐reported alcohol consumption. In: Litten RZ, Allen JP editor(s). Measuring Alcohol Consumption: Psychosocial and Biochemical Methods. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press Inc, 1992:41‐72.
Sobell 1995
-
- Sobell LC, Sobell MB. Alcohol consumption measures. In: Allen JP, Columbus M editor(s). Assessing Alcohol Problems: A Guide for Clinicians and Researchers. Rockville MD: National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, 1995:55‐73.
Spielberger 1970
-
- Spielberger CD, Gorsuch R, Lushene RE. Manual for the Trait‐State Anxiety Inventory. Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychlogists, 1970.
Spielberger 1983
-
- Spielberger CD, Gorsuch RL, LuShene R, Vagg PR, Jacobs GA. Manual for The State‐Trait Anxiety Inventory STAI (Form Y). Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press, 1983.
Spitzer 1981
-
- Spitzer WO, Dobson AJ, Hall J, Chesterman E, Levi J, Shepherd R, et al. Measuring the quality of life of cancer patients: a conciseQL‐index for use by physicians. Journal of Chronic Diseases 1981;34:585‐97. - PubMed
Spitzer 1990
-
- Spitzer RL, Williams JBW, Gibbon M, First MB. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM‐111‐R (SCID). Washington, DC: American PsychiatricAssociation, 1990.
Spitzer 1992
-
- Spitzer RL, Williams JB, Gibbon M, First MB. The structured clinical interview for DSM‐III‐R (SCID) I. History, rationales and description. Archives of General Psychiatry 1992;49:624‐9. - PubMed
Srisurapanont 2005
Stockwell 1983
-
- Stockwell T, Murphy D, Hodgson R. The severity of alcohol dependence questionnaire—Its use reliability and validity. British Journal of Addiction 1983;78:145‐55. - PubMed
Stout 1994
-
- Stout RL, Wirtz PW, Carbonari JP, Boca FK. Ensuring balanced distribution of prognostic factors in treatment outcome research. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs 1994;S 12:70‐5. - PubMed
Sullivan 1989
-
- Sullivan JT, Sykora K, Schneiderman J, Naranjo CA, Sellers EM. Assessment of alcohol withdrawal: the revised Clinical Institute Withdrawal Assessment for Alcohol scale (CIWA‐Ar). British Journal of Addiction 1989;84:1353‐7. - PubMed
Swendsen 1998
-
- Swendsen JD, Merikangas KR, Canino GJ, Kessler RC, Rubio‐Stipec M, Angst J. The comorbidity of alcoholism with anxiety and depressive disorders in four geographic communities. Comprehensive Psychiatry 1998;39:176‐84. - PubMed
Szabo 1996
-
- Szabo S. The World Health Organization Quality of Life (WHOQOL). In: Spiker B editor(s). Quality of Life and Pharmacoeconomics in Clinical Trials. Philadelphia: Lippincott‐Raven Publishers, 1996:355–362..
Thase 1983
-
- Thase ME, Hersen M, Bellack AS, Himmelhoch JM, Kupfer DJ. Validation of a Hamilton subscale for endogenomorphic depression. Journal of Affective Disorders 1983;5:267‐78. - PubMed
Volkow 2003
Volpicelli 2001
-
- Volpicelli JR, Pettinati HM, McLellan AT, McLellan T, O’Brien CHP. Enhanced medication and treatment adherence for addiction treatment: the BRENDA model. New York: Guilford Press, 2001.
Weiss 2003
-
- Weiss RD, Griffin ML, Mazurick C, Berkman B, Gastfriend DR, Frank A, et al. The relationship between cocaine craving, psychosocial treatment, and subsequent cocaine use. American Journal of Psychiatry 2003;160:1320‐5. - PubMed
Weiss 2006
-
- Weiss RD, Kueppenbender KD. Combining psychosocial treatment with pharmacotherapy for alcohol dependence. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2006;26(Suppl 1):S37‐S42. - PubMed
WHO 1992
-
- World Health Organization. The ICD‐10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders: Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Guidelines. Geneva: World Health Organization, 1992.
WHO 2004
-
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Alcohol. Geneva: WHO, 2004.
WHO 2011
-
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health. Geneva: WHO, 2011.
Williams 1988
-
- Williams JBW. A structured interview guide for the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale. Archives of General Psychiatry 1988;45:742‐7. - PubMed
Wing 1990
-
- Wing JK, Babor T, Brugha T, Burke J, Cooper JE, Giel R, et al. SCAN. Schedules for Clinical Assessment in Neuropsychiatry. Archives of General Psychiatry 1990;47:589‐93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

