Extracellular DNA can preserve the genetic signatures of present and past viral infection events in deep hypersaline anoxic basins
- PMID: 24523277
- PMCID: PMC4027399
- DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2013.3299
Extracellular DNA can preserve the genetic signatures of present and past viral infection events in deep hypersaline anoxic basins
Abstract
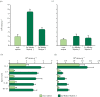
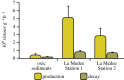
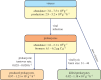
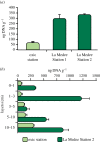
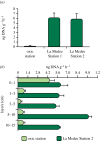
Deep hypersaline anoxic basins (DHABs) of the Mediterranean Sea are among the most extreme ecosystems on Earth and host abundant, active and diversified prokaryotic assemblages. However, factors influencing biodiversity and ecosystem functioning are still largely unknown. We investigated, for the first time, the impact of viruses on the prokaryotic assemblages and dynamics of extracellular DNA pool in the sediments of La Medee, the largest DHAB found on Earth. We also compared, in La Medee and L'Atalante sediments, the diversity of prokaryotic 16S rDNA sequences contained in the extracellular DNA released by virus-induced prokaryotic mortality. We found that DHAB sediments are hot-spots of viral infections, which largely contribute to the release of high amounts of extracellular DNA. DNase activities in DHAB sediments were much higher than other extracellular enzymatic activities, suggesting that extracellular DNA released from killed prokaryotes can be the most suitable trophic resource for benthic prokaryotes. Preserved extracellular DNA pools, which contained novel and diversified gene sequences, were very similar between the DHABs but dissimilar from the respective microbial DNA pools. We conclude that the strong viral impact in DHAB sediments influences the genetic composition of extracellular DNA, which can preserve the signatures of present and past infections.
Keywords: deep hypersaline anoxic basins; extracellular DNA; prokaryotes; viruses.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metazoans of redoxcline sediments in Mediterranean deep-sea hypersaline anoxic basins.BMC Biol. 2015 Dec 10;13:105. doi: 10.1186/s12915-015-0213-6. BMC Biol. 2015. PMID: 26652623 Free PMC article.
-
Viruses, prokaryotes and DNA in the sediments of a deep-hypersaline anoxic basin (DHAB) of the Mediterranean Sea.Environ Microbiol. 2005 Apr;7(4):586-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00727.x. Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15816935
-
Preservation, origin and genetic imprint of extracellular DNA in permanently anoxic deep-sea sediments.Mol Ecol. 2011 Feb;20(3):642-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04958.x. Epub 2010 Dec 14. Mol Ecol. 2011. PMID: 21155913
-
Deep Hypersaline Anoxic Basins as Untapped Reservoir of Polyextremophilic Prokaryotes of Biotechnological Interest.Mar Drugs. 2020 Jan 30;18(2):91. doi: 10.3390/md18020091. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32019162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbial ecology of deep-sea hypersaline anoxic basins.FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2018 Jul 1;94(7). doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiy085. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2018. PMID: 29905791 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Microbial Activity and Environmental Parameters on the Degradation of Extracellular Environmental DNA from a Eutrophic Lake.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Sep 10;16(18):3339. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16183339. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31510040 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics for Marine Products: An Overview of Resources, Bottlenecks, and Perspectives.Mar Drugs. 2019 Oct 11;17(10):576. doi: 10.3390/md17100576. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31614509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How, When, and Where Relic DNA Affects Microbial Diversity.mBio. 2018 Jun 19;9(3):e00637-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00637-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 29921664 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiling of microbial activities and interactions in sediments under haloclines of E. Mediterranean deep hypersaline anoxic basins.ISME J. 2016 Nov;10(11):2643-2657. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2016.58. Epub 2016 Apr 19. ISME J. 2016. PMID: 27093045 Free PMC article.
-
Viruses-to-mobile genetic elements skew in the deep Atlantis II brine pool sediments.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 6;6:32704. doi: 10.1038/srep32704. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27596223 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Lange GJ, et al. 1990. Composition of anoxic hypersaline brines in the Tyro and Bannock basins, Eastern Mediterranean. Mar. Chem. 31, 63–88. (10.1016/0304-4203(90)90031-7) - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

