Reservoir targeted vaccine against Borrelia burgdorferi: a new strategy to prevent Lyme disease transmission
- PMID: 24523510
- PMCID: PMC4038139
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiu005
Reservoir targeted vaccine against Borrelia burgdorferi: a new strategy to prevent Lyme disease transmission
Abstract
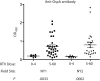
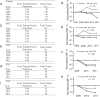
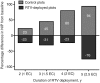
A high prevalence of infection with Borrelia burgdorferi in ixodid ticks is correlated with a high incidence of Lyme disease. The transmission of B. burgdorferi to humans can be disrupted by targeting 2 key elements in its enzootic cycle: the reservoir host and the tick vector. In a prospective 5-year field trial, we show that oral vaccination of wild white-footed mice resulted in outer surface protein A-specific seropositivity that led to reductions of 23% and 76% in the nymphal infection prevalence in a cumulative, time-dependent manner (2 and 5 years, respectively), whereas the proportion of infected ticks recovered from control plots varied randomly over time. Significant decreases in tick infection prevalence were observed within 3 years of vaccine deployment. Implementation of such a long-term public health measure could substantially reduce the risk of human exposure to Lyme disease.
Keywords: Borrelia burgdorferi; Lyme disease; Oral vaccine; enzootic cycle; transmission; wildlife reservoir.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Kurtenbach K, Hanincova K, Tsao JI, Margos G, Fish D, Ogden NH. Fundamental processes in the evolutionary ecology of Lyme borreliosis. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2006;4:660–9. - PubMed
-
- Dolan MC, Maupin GO, Schneider BS, et al. Control of immature Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae) on rodent reservoirs of Borrelia burgdorferi in a residential community of southeastern Connecticut. J Med Entomol. 2004;41:1043–54. - PubMed
-
- Gomes-Solecki MJ, Brisson DR, Dattwyler RJ. Oral vaccine that breaks the transmission cycle of the Lyme disease spirochete can be delivered via bait. Vaccine. 2006;24:4440–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

