Ribosomal alteration-derived signals for cytokine induction in mucosal and systemic inflammation: noncanonical pathways by ribosomal inactivation
- PMID: 24523573
- PMCID: PMC3910075
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/708193
Ribosomal alteration-derived signals for cytokine induction in mucosal and systemic inflammation: noncanonical pathways by ribosomal inactivation
Abstract
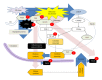
Ribosomal inactivation damages 28S ribosomal RNA by interfering with its functioning during gene translation, leading to stress responses linked to a variety of inflammatory disease processes. Although the primary effect of ribosomal inactivation in cells is the functional inhibition of global protein synthesis, early responsive gene products including proinflammatory cytokines are exclusively induced by toxic stress in highly dividing tissues such as lymphoid tissue and epithelia. In the present study, ribosomal inactivation-related modulation of cytokine production was reviewed in leukocyte and epithelial pathogenesis models to characterize mechanistic evidence of ribosome-derived cytokine induction and its implications for potent therapeutic targets of mucosal and systemic inflammatory illness, particularly those triggered by organellar dysfunctions.
Figures
References
-
- Deisenroth C, Zhang Y. Ribosome biogenesis surveillance: probing the ribosomal protein-Mdm2-p53 pathway. Oncogene. 2010;29(30):4253–4260. - PubMed
-
- Zhang F, Hamanaka RB, Bobrovnikova-Marjon E, et al. Ribosomal stress couples the unfolded protein response to p53-dependent cell cycle arrest. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2006;281(40):30036–30045. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources