Performance evaluation of a novel potentiometric membrane sensor for determination of atorvastatin in pharmaceutical preparations
- PMID: 24523744
- PMCID: PMC3920707
Performance evaluation of a novel potentiometric membrane sensor for determination of atorvastatin in pharmaceutical preparations
Abstract
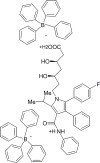
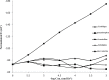
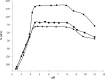
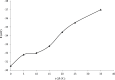
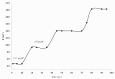
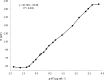
A novel potentiometric ion-selective PVC membrane sensor for analysis of atorvastatin (AT) in pharmaceutical preparations based on atorvastatin-(tetraphenyl borate), (AT-(TPB)2) as sensing element, tetraphenyl borate as additive and tris-2-ethyl-hexyl phosphate (TOP) as plasticizer solvent was prepared. The electrode shows a good Nernestian response over the concentration range of 0.09-5586 μg mL(-1)of AT with slope of 30.1±0.1 mV/decade and limit of detection0.056μg mL(-1).The response time of sensor is fats (less than 10 sec) and could be used for about one month in the pH range of 4.5-8.0. The electrode exhibit good selectivity for the AT in the presence of large amount of co-drugs and inorganic cations. The method is precise and accurate with mean relative standard deviation of <2%.Atorvastatin is determined successfully in several tablets by the proposed membrane.
Keywords: Analysis of pharmaceutical preparation; Atorvastatin; PVC membrane; Potentiometric sensor.
Figures
References
-
- Lea AP, Mc Tavish D, Atorvastatin A review of its pharmacology and therapeutic potential in the management of hyperlipidaemias. Drugs. 1997;53:828–847. - PubMed
-
- Ness GC, Chambers CM, Lopez D. Atorvastatin action involves diminished recovery of hepatic HMG-CoA reductase activity. J. Lipid. 1998;39:75–84. - PubMed
-
- Conde K, Pineda G, Newton RS, Fernandez ML. Hypocholesterolemic effects of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors in the guinea pig: Atorvastatin versus simvastatin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999;58:1209–1219. - PubMed
-
- Nawrocki JW, Weiss SR, Davidson MH, Sprecher DL, Schwartz SL, Lupien PJ, Jones PH, Haber HE, Black DM. Reduction of LDL cholesterol by 25% to 60% in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia by atorvastatin, a new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1995;15:678–682. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
