Triterpenes and Steroids from Euphorbia denticulata Lam. With Anti-Herpes Symplex Virus Activity
- PMID: 24523756
- PMCID: PMC3920720
Triterpenes and Steroids from Euphorbia denticulata Lam. With Anti-Herpes Symplex Virus Activity
Abstract
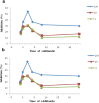
In this research, dried acetone:chloroform extract of aerial parts of E. denticulata as one of the endemic plants to Iran, afforded a number of triterpenes and steroids including: betulin, 24-methylene-cycloart-3-ol, cycloart-23Z-ene-3β,25-diol, cycloart-23E-ene-3β,25- diol, ergosta-8,24-dien-3-ol (obtusifoliol) and beta-sitosterol which were reported for the first time from this plant. The structure of these compounds was elucidated by NMR and mass spectroscopic methods. The MTS assay was used to determine the toxicity and antiviral activity of betulin and (3β,23E)-cycloarta-23-ene-3,25-diol. Betulin showed anti-HSV-1 activity with EC50 value of 84.37±0.02 μg/mL, and toxicity on normal vero cells with CC50 value of 660.718±0.072 μg/mL. (3β,23E)-Cycloarta-23-ene-3,25-diol showed antiviral effect with EC50 value of 86.63±0.03 μg/mL, and toxicity with CC50 value of 1089.21±0.25 μg/mL. The results revealed that these two compounds have the antiviral activity far below the CC50 value with selectivity index (CC50/EC50) values of 7.83, and 12.57, respectively.
Keywords: Euphorboa denticulate; anti- HSV-1 activity; cycloartanes; steroids; toxicity; triterpenes.
Figures

References
-
- Heywood VH, editor. Flowering Plants of the World. London: BT Batsford Ltd; 1998. pp. 183–187.
-
- Avicenna A. In: Ghanoon dar teb [The Canon of Medicine] Sharafkandi A, translator and editor. Vol. 5. Tehran: Soroush Press; 1998. pp. 410–413.
-
- Ramezani M, Behravan M, Arab M, Amel S. Antiviral avtivity of Euphorbia heliscopia extract. J. Biol. Sci. 2008;8:809–813.
-
- Gyuris A, Szlávik L, Minárovits J, Vasas A, Molnár J, Hohmann J. Antiviral activities of extracts of Euphorbia hirta L against HIV-1, HIV-2 and SIVmac251. In-vivo. 2009;23:429–432. - PubMed
-
- Khan MT, Ather A, Thompson KD, Gambari R. Extracts and molecules from medicinal plants against herpes simplex viruses. Pharmacol. Res. Antiviral Res. 2005;67:107–119. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
