ROCK inhibition activates MCF-7 cells
- PMID: 24523903
- PMCID: PMC3921164
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088489
ROCK inhibition activates MCF-7 cells
Abstract
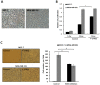
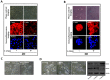
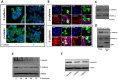
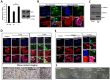
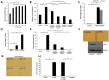
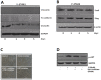
Dormant carcinoma cancer cells showing epithelial characteristics can be activated to dissipate into the surrounding tissue or organs through epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). However, the molecular details underlying the activation of dormant cancer cells have been less explored. In this study, we examined the molecular pathway to activate dormant breast cancer cells. Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) inhibition disrupted cell junction, promoted cell proliferation and migration / invasion in both two-dimensional and three-dimensional substrates. The disintegration of cell junction upon ROCK inhibition, coupled with the loss of E-cadherin and b-catenin from the cell membrane, was associated with the activation of Rac1 upon ROCK inhibition. Migration / invasion also increased upon ROCK inhibition. However, the activation of MCF-7 cells upon ROCK inhibition was not associated with the up-regulation of typical EMT markers, such as snail and slug. Based on these results, we suggest the potential risk for dormant cancer cells to dissipate through non-typical EMT when ROCK activity is down-regulated.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Trimboli AJ, Fukino K, de Bruin A, Wei G, Shen L, et al. (2008) Direct evidence for epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in breast cancer. Cancer Res 68: 937–945. - PubMed
-
- Paez D, Labonte MJ, Bohanes P, Zhang W, Benhanim L, et al. (2012) Cancer Dormancy: A Model of Early Dissemination and Late Cancer Recurrence. Clin Cancer Res 18: 645–653. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

