Healthy homes: in-home environmental asthma intervention in a diverse urban community
- PMID: 24524511
- PMCID: PMC4025713
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2013.301695
Healthy homes: in-home environmental asthma intervention in a diverse urban community
Abstract
Objectives: We evaluated health outcomes associated with in-home interventions in low-income urban households with children with asthma.
Methods: A comprehensive health and environmental assessment and subsequent intervention were completed in 116 households with 170 enrolled children with asthma. Home health workers provided household safety, asthma prevention education, and targeted environmental intervention to decrease asthma triggers and improve household safety. We collected environmental data with questionnaire and dust samples and health information with a questionnaire incorporating the American Academy of Pediatrics Children's Health Survey for Asthma and other instruments at baseline and at follow-up 11 to 12 months later to evaluate the impact of the intervention on the health of the child and family in Lowell, Massachusetts, from September 2009 to January 2012.
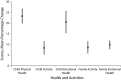
Results: The diverse study population of low-income children showed a statistically significant health improvement from baseline to follow-up. The cost of the interventions (not including personnel) was $36 240, whereas the estimated medical savings over a 4-week assessment period was $71 162, resulting in an estimated annual savings of about $821 304.
Conclusions: Low-cost, multicomponent interventions decrease all measures of asthma severity and health care utilization in a diverse population of urban children.
Figures
References
-
- Etzel RA. How environmental exposures influence the development and exacerbation of asthma. Pediatrics. 2003;112(1 pt 2):233–239. - PubMed
-
- Takaro TK, Krieger JW, Song L. Effects of environmental interventions to reduce exposure to asthma triggers in homes of low-income children in Seattle. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol. 2004;14(suppl 1):S133–S143. - PubMed
-
- Akinbami LJ, Moorman JE, Liu X. Asthma prevalence, health care use and mortality: United States, 2005–2009. Natl Health Stat Reports. 2011;(32):1–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical