Disrupting the interaction of BRD4 with diacetylated Twist suppresses tumorigenesis in basal-like breast cancer
- PMID: 24525235
- PMCID: PMC4004960
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.01.028
Disrupting the interaction of BRD4 with diacetylated Twist suppresses tumorigenesis in basal-like breast cancer
Abstract
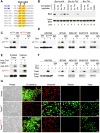
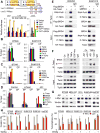
Twist is a key transcription activator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). It remains unclear how Twist induces gene expression. Here we report a mechanism by which Twist recruits BRD4 to direct WNT5A expression in basal-like breast cancer (BLBC). Twist contains a "histone H4-mimic" GK-X-GK motif that is diacetylated by Tip60. The diacetylated Twist binds the second bromodomain of BRD4, whose first bromodomain interacts with acetylated H4, thereby constructing an activated Twist/BRD4/P-TEFb/RNA-Pol II complex at the WNT5A promoter and enhancer. Pharmacologic inhibition of the Twist-BRD4 association reduced WNT5A expression and suppressed invasion, cancer stem cell (CSC)-like properties, and tumorigenicity of BLBC cells. Our study indicates that the interaction with BRD4 is critical for the oncogenic function of Twist in BLBC.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists
Figures





References
-
- Brunger AT. X-PLOR version 3.1: A system for X-ray Crystallography and NMR (version 3.1 edit) Yale University Press; New Haven, CT: 1993.
-
- Clore GM, Gronenborn AM. Multidimensional heteronuclear nuclear magnetic resonance of proteins. Methods in enzymology. 1994;239:349–363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

